GL-II-73
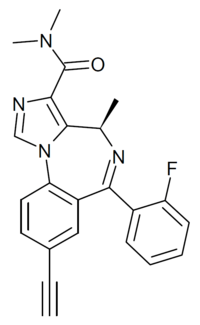
GL-II-73 (GL-ii-073) is a benzodiazepine derivative related in chemical structure to compounds such as midazolam, adinazolam and the active metabolite of rilmazafone. It is described as an α5 preferring positive allosteric modulator of the benzodiazepine site of GABAA receptors, with weaker activity at α2 and α3 and no significant affinity for the α1 subtype. In animal tests it was found to produce effects consistent with antidepressant, anxiolytic and nootropic actions.[1][2][3][4]
 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
IUPAC name
| |
| PubChem CID | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C23H19FN4O |
| Molar mass | 386.430 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
References
- Cook JM, Li G, Poe M, Savic M, Sibille E. Treatment of cognitive and mood symptoms in neurodegenerative and neuropsychiatric disorders with alpha5-containing gabaa receptor agonists. Patent application CA3016491
- Prevot TD, et al. Potential combined pro-cognitive, anxiolytic and antidepressant properties of novel GABAA receptor positive modulators with preferential efficacy at the α5-subunit. BioRxiv 2018 doi:10.1101/332908
- Prevot TD, et al. Novel Benzodiazepine-Like Ligands with Various Anxiolytic, Antidepressant, or Pro-Cognitive Profiles. Molecular Neuropsychiatry, 2019; 1. doi:10.1159/000496086
- Etienne Sibille. Brain Inhibitory GABAergic Function and Cognitive Deficits: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Targeting. Presentation for AAAS, Feb 2019.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative
Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.