Devazepide
Devazepide[1] (L-364,718, MK-329) is benzodiazepine drug, but with quite different actions from most benzodiazepines, lacking affinity for GABAA receptors and instead acting as an CCKA receptor antagonist.[2] It increases appetite and accelerates gastric emptying,[3][4] and has been suggested as a potential treatment for a variety of gastrointestinal problems including dyspepsia, gastroparesis and gastric reflux.[5] It is also widely used in scientific research into the CCKA receptor.[6][7]
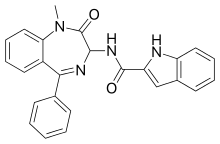 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.208.547 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C25H20N4O2 |
| Molar mass | 408.452 g/mol g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| | |
See also
References
- US Patent 4820834
- Hill, DR; Woodruff, GN (Sep 1990). "Differentiation of central cholecystokinin receptor binding sites using the non-peptide antagonists MK-329 and L-365,260". Brain Research. 526 (2): 276–83. doi:10.1016/0006-8993(90)91232-6. PMID 2257485.
- Cooper, SJ; Dourish, CT (Dec 1990). "Multiple cholecystokinin (CCK) receptors and CCK-monoamine interactions are instrumental in the control of feeding". Physiology & Behavior. 48 (6): 849–57. doi:10.1016/0031-9384(90)90239-z. PMID 1982361.
- Cooper, SJ; Dourish, CT; Clifton, PG (January 1992). "CCK antagonists and CCK-monoamine interactions in the control of satiety". Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 55: 291S–295S. PMID 1728842.
- Scarpignato, C; Varga, G; Corradi, C (1993). "Effect of CCK and its antagonists on gastric emptying". Journal of Physiology, Paris. 87 (5): 291–300. doi:10.1016/0928-4257(93)90035-r. PMID 8298606.
- Weller, A (Jul 2006). "The ontogeny of postingestive inhibitory stimuli: examining the role of CCK". Developmental Psychobiology. 48 (5): 368–79. doi:10.1002/dev.20148. PMID 16770766.
- Savastano, DM; Covasa, M (Oct 2007). "Intestinal nutrients elicit satiation through concomitant activation of CCK(1) and 5-HT(3) receptors". Physiology & Behavior. 92 (3): 434–42. doi:10.1016/j.physbeh.2007.04.017. PMID 17531277.
- "Methods for drug discovery: development of potent, selective, orally effective cholecystokinin antagonists". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 31: 2235–2246. doi:10.1021/jm00120a002.
- EP 1492540
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative
Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.