Pentagastrin
Pentagastrin (trade name Peptavlon) is a synthetic polypeptide that has effects like gastrin when given parenterally.[2] It stimulates the secretion of gastric acid, pepsin, and intrinsic factor, and has been used as a diagnostic aid as the pentagastrin-stimulated calcitonin test.
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Micromedex Detailed Consumer Information |
| ATC code | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Elimination half-life | 10 minutes or less |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.024.445 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
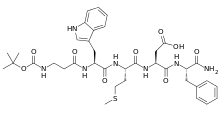
| Formula | C37H49N7O9S |
| Molar mass | 767.893 g/mol g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| (verify) | |
Pentagastrin binds to the cholecystokinin-B receptor, which is expressed widely in the brain. Activation of these receptors activates the phospholipase C second messenger system. When given intravenously it may cause panic attacks.[3]
Pentagastrin's IUPAC chemical name is "N-((1,1-dimethylethoxy)carbonyl)-beta-alanyl-L-tryptophyl-L-methionyl-L-alpha-aspartyl-L-phenylalaninamide".
Pentagastrin stimulation test
Pentagastrin is also used as a stimulation test to elevate of several hormones, such as serotonin. It provokes flushing and is useful in evaluating patients who describe flushing, but have normal or only marginally elevated biochemical markers for carcinoid syndrome.
It has been used to stimulate ectopic gastric mucosa for the detection of Meckels diverticulum by nuclear medicine.
Calcitonin test
The pentagastrin-stimulated calcitonin test is a diagnostic test for medullary carcinoma of the thyroid (MTC). MTC is a malignancy of the calcitonin-secreting cells of the thyroid gland, and thus MTC is commonly associated with an elevated calcitonin level, but an elevated level may not always be obvious. The pentagastrin-stimulated calcitonin test is useful in cases of suspected MTC that are not associated with elevated calcitonin. In these patients, injecting pentagastrin will cause calcitonin levels to rise significantly above the normal or basal range.[4] After a total thyroidectomy for medullary thyroid carcinoma, the pentagastrin-stimulated calcitonin release can be used to detect residual parafollicular C-cells.
See also
References
- Martindale (1993). The extra pharmacopoeia (30th ed.). London: Pharmaceutical Press. ISBN 978-0853693000.
- Braganza, J. M.; Herman, K; Hine, P; Kay, G (1979). "The effect of pentagastrin on peptic secretion in man". The Journal of Physiology. 289: 9–16. doi:10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012721. PMC 1281354. PMID 379305.
- van Megen, HJ; Westenberg, HG; den Boer, JA; Haigh, JR; Traub, M (April 1994). "Pentagastrin induced panic attacks: enhanced sensitivity in panic disorder patients". Psychopharmacology. 114 (3): 449–55. doi:10.1007/bf02249335. PMID 7855203.
- Barbot, N; Calmettes, C; Schuffenecker, I; Saint-André, J P; Franc, B; Rohmer, V; Jallet, P; Bigorgne, J C (January 1994). "Pentagastrin stimulation test and early diagnosis of medullary thyroid carcinoma using an immunoradiometric assay of calcitonin: comparison with genetic screening in hereditary medullary thyroid carcinoma". The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism. 78 (1): 114–120. doi:10.1210/jcem.78.1.7904611. PMID 7904611.