Teriparatide
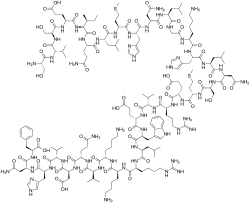
Teriparatide is a form of parathyroid hormone consisting of the first (N-terminus) 34 amino acids, which is the bioactive portion of the hormone. It is an effective anabolic (promoting bone formation) agent[2] used in the treatment of some forms of osteoporosis.[3] It is also occasionally used off-label to speed fracture healing. Teriparatide is identical to a portion of human parathyroid hormone (PTH) and intermittent use activates osteoblasts more than osteoclasts, which leads to an overall increase in bone.
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Forteo/Forsteo, Teribone[1] |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| License data | |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | Subcutaneous |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 95% |
| Metabolism | Hepatic (nonspecific proteolysis) |
| Elimination half-life | Subcutaneous: 1 hour |
| Excretion | Renal (metabolites) |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.168.733 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C181H291N55O51S2 |
| Molar mass | 4117.72 g/mol g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| | |
Recombinant teriparatide is sold by Eli Lilly and Company under the brand name Forteo/Forsteo. A synthetic teriparatide from Teva Generics has been authorised for marketing in European territories[4]. Biosimilar product from Gedeon Richter plc has been authorised in Europe[5]. On October 4, 2019 the US FDA approved a recombinant teriparatide product, PF708, from Pfenex Inc. PF708 is the first FDA approved proposed therapeutic equivalent candidate to Forteo.
Medical uses
Teriparatide has been FDA-approved since 2002.[6] It is effective in growing bone (e.g., 8% increase in bone density in the spine after one year)[7] and reducing the risk of fragility fractures.[6][8] When studied, teriparatide only showed bone mineral density (BMD) improvement during the first 18 months of use. Teriparatide should only be used for a period of 2 years maximum. After 2 years, another agent such a bisphosphonate or denosumab should be used in cases of osteoporosis. [9]
Teriparatide cuts the risk of hip fracture by more than half but does not reduce the risk of arm or wrist fracture.[10]
Other
Teriparatide can be used off-label to speed fracture repair and treat fracture nonunions.[11] It has been reported to have been successfully used to heal fracture nonunions.[12] Generally, due to HIPAA regulations, it is not publicized when American athletes receive this treatment to improve fracture recovery.[11] But an Italian football player, Francesco Totti, was given teriparatide after a tibia/fibula fracture, and he unexpectedly recovered in time for the 2006 World Cup.[11] It has been reported that Mark Mulder used it to recover from a hip fracture Oakland A's for the 2003 MLB playoffs[13] and Terrell Owens to recover from an ankle fracture before the 2005 Super Bowl.[13]
Administration
Teriparatide is administered by injection once a day in the thigh or abdomen.
Contraindications
Teriparatide should not be prescribed for people who are at increased risks for osteosarcoma. This includes those with Paget's Disease of bone or unexplained elevations of serum alkaline phosphate, open epiphysis, or prior radiation therapy involving the skeleton. In the animal studies and in one human case report, it was found to potentially be associated with developing osteosarcoma in test subjects after over 2 years of use. [14]
Patients should not start teriparatide until any vitamin D deficiency is corrected. [15]
Adverse effects
Adverse effects of teriparatide include headache, nausea, dizziness, and limb pain.[6] Teriparatide has a theoretical risk of osteosarcoma, which was found in rat studies but not confirmed in humans.[2] This may be because unlike humans, rat bones grow for their entire life.[2] The tumors found in the rat studies were located on the end of the bones which grew after the injections began.[15] After nine years on the market, there were only two cases of osteosarcoma reported.[7] This risk was considered by the FDA as "extremely rare" (1 in 100,000 people)[6] and is only slightly more than the incidence in the population over 60 years old (0.4 in 100,000).[6]
Mechanism of action
Teriparatide is a portion of human parathyroid hormone (PTH), amino acid sequence 1 through 34, of the complete molecule (containing 84 amino acids). Endogenous PTH is the primary regulator of calcium and phosphate metabolism in bone and kidney. PTH increases serum calcium, partially accomplishing this by increasing bone resorption. Thus, chronically elevated PTH will deplete bone stores. However, intermittent exposure to PTH will activate osteoblasts more than osteoclasts. Thus, once-daily injections of teriparatide have a net effect of stimulating new bone formation leading to increased bone mineral density.[16][17][18]
Teriparatide is the first FDA approved agent for the treatment of osteoporosis that stimulates new bone formation.[19]
FDA approval
Teriparatide was approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) on 26 November 2002, for the treatment of osteoporosis in men and postmenopausal women who are at high risk for having a fracture. The drug is also approved to increase bone mass in men with primary or hypogonadal osteoporosis who are at high risk for fracture.
Combined teriparatide and denosumab
Combined teriparatide and denosumab increased BMD more than either agent alone and more than has been reported with approved therapies. Combination treatment might, therefore, be useful to treat patients at high risk of fracture by increasing BMD. However, there is no evidence of fracture rate reduction in patients taking a teriparatide and denosumab combination. Moreover, the combination therapy group showed a significant decrease in their bone formation marker, indicating that denosumab, an antiresorptive agent, might actually counteract the effect of teriparatide, a bone formation anabolic agent, in bone formation. [20]
See also
- Abaloparatide
- Osteolectin
References
- http://www.minsa.gob.pa/sites/default/files/alertas/nota_seguridad_teriparatida.pdf
- Riek AE and Towler DA (2011). "The pharmacological management of osteoporosis". Missouri Medicine. 108 (2): 118–23. PMC 3597219. PMID 21568234.CS1 maint: uses authors parameter (link)
- Saag KG, Shane E, Boonen S, et al. (November 2007). "Teriparatide or alendronate in glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis". The New England Journal of Medicine. 357 (20): 2028–39. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa071408. PMID 18003959.
- BfArM (2017-05-08). "PUBLIC ASSESSMENT REPORT - Decentralised Procedure - Teriparatid-ratiopharm 20 µg / 80ml, Solution for injection" (PDF).
- "Summary of the European public assessment report (EPAR) for Terrosa". Retrieved 2019-08-14.
- Rizzoli, R.; Reginster, J. Y.; Boonen, S.; Bréart, G. R.; Diez-Perez, A.; Felsenberg, D.; Kaufman, J. M.; Kanis, J. A.; Cooper, C. (2011). "Adverse Reactions and Drug–Drug Interactions in the Management of Women with Postmenopausal Osteoporosis". Calcified Tissue International. 89 (2): 91–104. doi:10.1007/s00223-011-9499-8. PMC 3135835. PMID 21637997.
- Kawai, M.; Mödder, U. I.; Khosla, S.; Rosen, C. J. (2011). "Emerging therapeutic opportunities for skeletal restoration". Nature Reviews Drug Discovery. 10 (2): 141–156. doi:10.1038/nrd3299. PMC 3135105. PMID 21283108.
- Murad, M. H.; Drake, M. T.; Mullan, R. J.; Mauck, K. F.; Stuart, L. M.; Lane, M. A.; Abu Elnour, N. O.; Erwin, P. J.; Hazem, A.; Puhan, M. A.; Li, T.; Montori, V. M. (2012). "Comparative Effectiveness of Drug Treatments to Prevent Fragility Fractures: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis". Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism. 97 (6): 1871–1880. doi:10.1210/jc.2011-3060. PMID 22466336.
- O'Connor KM. Evaluation and Treatment of Osteoporosis. Med Clin N Am. 2016; 100:807-26
- Díez-Pérez A, Marin F, Eriksen EF, Kendler DL, Krege JH, Delgado-Rodríguez M (September 2018). "Effects of teriparatide on hip and upper limb fractures in patients with osteoporosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis". Bone. 120: 1–8. doi:10.1016/j.bone.2018.09.020. PMID 30268814.
- Bruce Jancin (2011-12-12). "Accelerating Fracture Healing With Teriparatide". Internal Medicine News Digital Network. Retrieved 2013-09-20.
- Giannotti, S.; Bottai, V.; Dell’Osso, G.; Pini, E.; De Paola, G.; Bugelli, G.; Guido, G. (2013). "Current medical treatment strategies concerning fracture healing". Clinical Cases in Mineral and Bone Metabolism. 10 (2): 116–120. PMC 3796998. PMID 24133528.
- William L. Carroll (2005). "Chapter 1: Defining the Issue". The Juice: The Real Story of Baseball's Drug Problems. ISBN 1-56663-668-X. Retrieved 2013-09-23.
- Harper KD, Krege JH, Marcus R, et al. Osteosarcoma and teriparatide? J Bone Miner Res 2007;22(2):334
- https://www.drugs.com/pro/forteo.html
- Bauer, E; Aub, JC; Albright, F (1929). "Studies of calcium and phosphorus metabolism: V. Study of the bone trabeculae as a readily available reserve supply of calcium". J Exp Med. 49 (1): 145–162. doi:10.1084/jem.49.1.145. PMC 2131520. PMID 19869533.
- Selye, H (1932). "On the stimulation of new bone formation with parathyroid extract and irradiated ergosterol". Endocrinology. 16 (5): 547–558. doi:10.1210/endo-16-5-547.
- Dempster, D. W.; Cosman, F.; Parisien, M.; Shen, V.; Lindsay, R. (1993). "Anabolic actions of parathyroid hormone on bone". Endocrine Reviews. 14 (6): 690–709. doi:10.1210/edrv-14-6-690. PMID 8119233.
- Fortéo: teriparatide (rDNA origin) injection Archived 2009-12-27 at the Wayback Machine
- Tsai, Joy N; Uihlein, Alexander V; Lee, Hang; Kumbhani, Ruchit; Siwila-Sackman, Erica; McKay, Elizabeth A; Burnett-Bowie, Sherri-Ann M; Neer, Robert M; Leder, Benjamin Z (2013). "Teriparatide and denosumab, alone or combined, in women with postmenopausal osteoporosis: The DATA study randomised trial". The Lancet. 382 (9886): 1694–1700. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(13)60856-9. PMC 4010689. PMID 24517156.