Testosterone butyrate
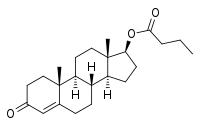
Testosterone butyrate, or testosterone butanoate, also known as androst-4-en-17β-ol-3-one 17β-butanoate, is a synthetic, steroidal androgen and an androgen ester – specifically, the C17β butanoate ester of testosterone – which was first synthesized in the 1930s and was never marketed.[1][2][3][4] Its ester side-chain length and duration of effect are intermediate between those of testosterone propionate and testosterone valerate.[2]
| Medication | Form | Major brand names | Duration |
|---|---|---|---|
| Testosterone | Aqueous suspension | Andronaq, Sterotate, Virosterone | 2–3 days |
| Testosterone propionate | Oil solution | Androteston, Perandren, Testoviron | 3–4 days |
| Testosterone phenylpropionate | Oil solution | Testolent | 8 days |
| Testosterone isobutyrate | Aqueous suspension | Agovirin Depot, Perandren M | 14 days |
| Mixed testosterone estersa | Oil solution | Triolandren | 10–20 days |
| Mixed testosterone estersb | Oil solution | Testosid Depot | 14–20 days |
| Testosterone enanthate | Oil solution | Delatestryl | 14–20 days |
| Testosterone cypionate | Oil solution | Depovirin | 14–20 days |
| Mixed testosterone estersc | Oil solution | Sustanon 250 | 28 days |
| Testosterone undecanoate | Oil solution | Aveed, Nebido | 100 days |
| Testosterone buciclated | Aqueous suspension | 20 Aet-1, CDB-1781e | 90–120 days |
| Nandrolone phenylpropionate | Oil solution | Durabolin | 10 days |
| Nandrolone decanoate | Oil solution | Deca Durabolin | 21 days |
| Methandriol | Aqueous suspension | Notandron, Protandren | 8 days |
| Methandriol bisenanthoyl acetate | Oil solution | Notandron Depot | 16 days |
| Metenolone acetate | Oil solution | Primobolan | 3 days |
| Metenolone enanthate | Oil solution | Primobolan Depot | 14 days |
| Note: All are via i.m. injection. Footnotes: a = TP, TV, and TUe. b = TP and TKL. c = TP, TPP, TiCa, and TD. d = Studied but never marketed. e = Developmental code names. Sources: See template. | |||
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Routes of administration | Intramuscular injection |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.020.270 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C23H34O3 |
| Molar mass | 358.522 g/mol g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
References
- Samuel H. Yalkowsky; Yan He; Parijat Jain (19 April 2016). Handbook of Aqueous Solubility Data, Second Edition. CRC Press. pp. 1288–. ISBN 978-1-4398-0246-5.
- Ralph Isadore Dorfman; Reginald A. Shipley (1956). Androgens: biochemistry, physiology, and clinical significance. Wiley. p. 119.
- Koch, F. C. (1937). "RECENT ADVANCES IN THE FIELD OF ANDROGENS". Cold Spring Harbor Symposia on Quantitative Biology. 5 (0): 34–43. doi:10.1101/SQB.1937.005.01.004. ISSN 0091-7451.
- Griffiths, P. J. F.; James, K. C.; Rees, M. (1965). "Crystallographic data for some testosterone esters". Acta Crystallographica. 19 (1): 149–150. doi:10.1107/S0365110X65002918. ISSN 0365-110X.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative
Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.