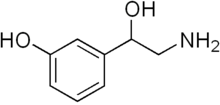
Norfenefrine
Norfenefrine (INN; also known as meta-octopamine, 3-octopamine, and 3,β-dihydroxyphenethylamine) is an adrenergic agent used as a sympathomimetic drug which is marketed in Europe, Japan, and Mexico.[1][2] Along with its structural isomer p-octopamine and the tyramines, norfenefrine is a naturally occurring, endogenous trace amine and plays a role as a minor neurotransmitter in the brain.[3]
 | |
-Norfenefrine_molecule_ball.png) | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Norfenephrine Norphenephrine Norphenylephrine meta-Norsynephrine meta-Octopamine 3-Octopamine |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number |
|
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.007.844 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C8H11NO2 |
| Molar mass | 153.181 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| | |
Some brand names for it include Coritat, Energona, Hypolind, and Novadral.
See also
References
- Macdonald F (1997). Dictionary of Pharmacological Agents. CRC Press. p. 104. ISBN 978-0-412-46630-4. Retrieved 24 April 2012.
- Index Nominum 2000: International Drug Directory. Taylor & Francis. 2000. p. 750. ISBN 978-3-88763-075-1. Retrieved 24 April 2012.
- Danielson TJ, Boulton AA, Robertson HA (December 1977). "m-Octopamine, p-octopamine and phenylethanolamine in rat brain: a sensitive, specific assay and the effects of some drugs". Journal of Neurochemistry. 29 (6): 1131–5. doi:10.1111/j.1471-4159.1977.tb06519.x. PMID 340613.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative
Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.