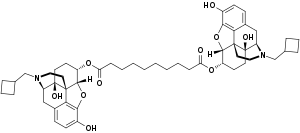
Dinalbuphine sebacate
Dinalbuphine sebacate (DNS), also known as nalbuphine sebacate or as sebacoyl dinalbuphine ester (SDE) and sold under the brand name Naldebain, is a non-controlled opioid analgesic which is used as a 7-day long-acting injection in the treatment of moderate to severe postoperative pain.[3][4][5] It was developed by Lumosa Therapeutics and was approved in Taiwan in the spring of 2017; development is ongoing in the United States.[3][4] The compound is a diester of nalbuphine (Nubain) joined via a sebacic acid linker, and acts as a long-lasting prodrug of nalbuphine via slow hydrolysis.[5][2][6] It was developed to extend the duration of action of nalbuphine, which has a short duration and requires frequent injections.[5][2][1] Whereas nalbuphine must be injected every 4 to 6 hours, a single injection of DNS lasts for up to 7 to 10 days.[5] Nalbuphine, and hence DNS, acts as a mixed agonist/antagonist opioid modulator, or more specifically as a moderate-efficacy partial agonist or antagonist of the μ-opioid receptor and as a high-efficacy partial agonist of the κ-opioid receptor.[5][7][8][9][10]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | DNS; Nalbuphine sebacate; Sebacoyldinalbuphine; SDN; Sebacoyl dinalbuphine ester; SDE; LT-1001 |
| Routes of administration | Intramuscular injection |
| Drug class | Opioid analgesic |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | • IM: 85.4% (relative to nalbuphine)[1] |
| Metabolism | Hydrolysis[2] |
| Metabolites | Nalbuphine[1] |
| Elimination half-life | • DNS: 83.2 hours (mean absorption time: 145.2 hours)[1] • Nalbuphine: 4.0 hours |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C52H68N2O10 |
| Molar mass | 881.12 g/mol g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
References
- Tien YE, Huang WC, Kuo HY, Tai L, Uang YS, Chern WH, Huang JD (November 2017). "Pharmacokinetics of dinalbuphine sebacate and nalbuphine in human after intramuscular injection of dinalbuphine sebacate in an extended-release formulation". Biopharm Drug Dispos. 38 (8): 494–497. doi:10.1002/bdd.2088. PMID 28741675.
- Pao LH, Hsiong CH, Hu OY, Wang JJ, Ho ST (March 2005). "In vitro and in vivo evaluation of the metabolism and pharmacokinetics of sebacoyl dinalbuphine". Drug Metab. Dispos. 33 (3): 395–402. doi:10.1124/dmd.104.002451. PMID 15608131.
- "Dinalbuphine sebacate - Lumosa Therapeutics - AdisInsight". adisinsight.springer.com.
- "Lumosa Therapeutics Partners with Camargo Pharmaceutical Services in the Development of Naldebain(R) in the US". www.prnewswire.com.
- Yeh CY, Jao SW, Chen JS, Fan CW, Chen HH, Hsieh PS, Wu CC, Lee CC, Kuo YH, Hsieh MC, Huang WS, Chung YC, Liou TY, Chiu HH, Tseng WK, Lee KC, Wang JY (May 2017). "Sebacoyl Dinalbuphine Ester Extended-release Injection for Long-acting Analgesia: A Multicenter, Randomized, Double-Blind, And Placebo-controlled Study in Hemorrhoidectomy Patients". Clin J Pain. 33 (5): 429–434. doi:10.1097/AJP.0000000000000417. PMID 27518486.
- Pao LH, Hsiong CH, Hu OY, Ho ST (September 2000). "High-performance liquid chromatographic method for the simultaneous determination of nalbuphine and its prodrug, sebacoyl dinalbuphine ester, in dog plasma and application to pharmacokinetic studies in dogs". J. Chromatogr. B. 746 (2): 241–7. doi:10.1016/S0378-4347(00)00326-1. PMID 11076077.
- Narver HL (March 2015). "Nalbuphine, a non-controlled opioid analgesic, and its potential use in research mice". Lab Anim (NY). 44 (3): 106–10. doi:10.1038/laban.701. PMID 25693108.
- Schmidt WK, Tam SW, Shotzberger GS, Smith DH, Clark R, Vernier VG (February 1985). "Nalbuphine". Drug Alcohol Depend. 14 (3–4): 339–62. doi:10.1016/0376-8716(85)90066-3. PMID 2986929.
- Paul G. Barash (2009). Clinical Anesthesia. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 489–. ISBN 978-0-7817-8763-5.
- Peng X, Knapp BI, Bidlack JM, Neumeyer JL (May 2007). "Pharmacological properties of bivalent ligands containing butorphan linked to nalbuphine, naltrexone, and naloxone at mu, delta, and kappa opioid receptors". J. Med. Chem. 50 (9): 2254–8. doi:10.1021/jm061327z. PMC 3357624. PMID 17407276.