Oliceridine
Oliceridine (developmental code name TRV-130; tentative brand name Olinvo) is an opioid drug that is under evaluation in human clinical trials for the intravenous treatment of severe acute pain. It is a μ-opioid receptor biased agonist developed by Trevena. In cell-based (in vitro) research, oliceridine elicits robust G protein signaling, with potency and efficacy similar to that of morphine, but with less β-arrestin 2 recruitment and receptor internalization—thus, it may have fewer adverse effects than morphine.[1][2][3][4] In general, in vitro potency does not guarantee any clinical relevance in humans.[5]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Olinvo |
| Other names | TRV-130 |
| Routes of administration | Intravenous |
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Identifiers | |
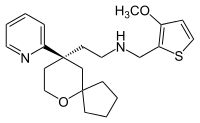
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C22H30N2O2S |
| Molar mass | 386.55 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
Society and culture
An FDA advisory committee voted against the approval of oliceridine in 2018, due to concerns that the benefit of the drug did not exceed the risk. The risks of oliceridine include prolongation of the QT interval on the ECG, and depression of the respiratory drive (which could cause a person to stop breathing).[6] As a result of the committee's vote, the FDA declined to approve oliceridine, citing safety concerns.[7]
See also
References
- Chen XT, Pitis P, Liu G, Yuan C, Gotchev D, Cowan CL, Rominger DH, Koblish M, Dewire SM, Crombie AL, Violin JD, Yamashita DS (subscription required) (October 2013). "Structure-Activity Relationships and Discovery of a G Protein Biased μ Opioid Receptor Ligand, [(3-Methoxythiophen-2-yl)methyl]({2-[(9R)-9-(pyridin-2-yl)-6-oxaspiro-[4.5]decan-9-yl]ethyl})amine (TRV130), for the Treatment of Acute Severe Pain". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 56 (20): 8019–31. doi:10.1021/jm4010829. PMID 24063433.CS1 maint: uses authors parameter (link)
- DeWire SM, Yamashita DS, Rominger DH, Liu G, Cowan CL, Graczyk TM, Chen XT, Pitis PM, Gotchev D, Yuan C, Koblish M, Lark MW, Violin JD (March 2013). "A G protein-biased ligand at the μ-opioid receptor is potently analgesic with reduced gastrointestinal and respiratory dysfunction compared with morphine". Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics. 344 (3): 708–17. doi:10.1124/jpet.112.201616. PMID 23300227.
- Soergel DG, Subach RA, Sadler B, Connell J, Marion AS, Cowan C, Violin JD, Lark MW (October 2013). "First clinical experience with TRV130: Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics in healthy volunteers". The Journal of Clinical Pharmacology. 54 (3): 351–7. doi:10.1002/jcph.207. PMID 24122908.
- Staff (1 October 2015). "Acute Postoperative Pain". Genetic Engineering & Biotechnology News (Paper). 35 (17): 40.
- Waldman, SA (July 2002). "Does potency predict clinical efficacy? Illustration through an antihistamine model". Annals of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology. 89 (1): 7–11, quiz 11-2, 77. doi:10.1016/S1081-1206(10)61904-7. PMID 12141724.
- "FDA Panel Votes Against Analgesic Oliceridine". www.medpagetoday.com. MedPage Today, LLC. 11 October 2018. Retrieved 23 December 2018.
- "FDA rejects Trevena's painkiller oliceridine | FierceBiotech". www.fiercebiotech.com. Questex LLC. Retrieved 23 December 2018.