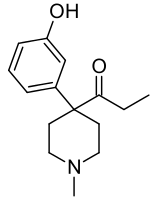
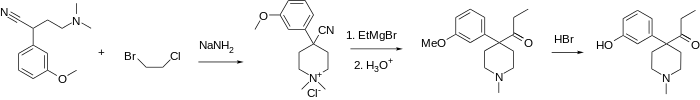Ketobemidone
Ketobemidone, sold under the brand name Ketogan among others, is a powerful synthetic opioid painkiller. Its effectiveness against pain is in the same range as morphine, and it also has some NMDA-antagonist properties imparted, in part, by its metabolite norketobemidone.[1] This may make it useful for some types of pain that do not respond well to other opioids.[1] It is marketed in Denmark, Norway and Sweden and is used for severe pain.[2]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Ketobemidone, Cliradon, Cymidon, Ketogan, Ketorax |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| Routes of administration | Oral, rectal, intravenous |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 34∼40% (oral), 44% (rectal) |
| Elimination half-life | 2–4 hours |
| Duration of action | 3–5 hours |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.006.748 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C15H21NO2 |
| Molar mass | 247.338 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| | |
History
Ketobemidone was first synthesized in 1942 by Eisleb and colleagues,[3] at the laboratory of I.G. Farbenindustrie at Hoechst during the Second World War. The first study of it in humans was published in 1946,[4] and it was introduced in clinical medicine shortly after. It was not in clinical use in the United States when the Controlled Substances Act 1970 was promulgated and was assigned to Schedule I with an ACSCN of 9628. As of 2013, no annual manufacturing quota was assigned by the DEA.[5]
Pfizer manufactures ketobemidone under the tradenames Ketogan and Ketorax. It is available as tablets, suppositories, and injection fluid. A sustained release formulation exists, sold as Ketodur, in some countries containing 10 or 25 mg ketobemidone.
Pharmacology
Experiments on former addicts indicated it was more addictive than other opioids, so in 1954 the Economic and Social Council took a resolution urging governments to stop manufacture and use of ketobemidone.[6] This result was not in agreement with clinical observations, and another study in 1958 did not find it more addictive than morphine. That study noticed that while for morphine the dose for euphoria is the same as that for analgesia, for ketobemidone the analgesic dose was well below the euphoric dose.[7] Ketobemidone is mostly used in the Scandinavian countries, with Denmark topping the statistics.[8]
Analgesia after 5-10 mg orally or 5-7.5 mg intravenously lasts 3–5 hours. Ketobemidone is also available in preparations with a spasmolytic, which can improve the analgesia.
Metabolism
Ketobemidone is mainly metabolized by conjugation of the phenolic hydroxyl group, and by N-demethylation. Only about 13-24% is excreted unchanged after intravenous administration.[9]
Chemistry
Ketobemidone is 1-methyl-4-(3-hydroxyphenyl)-4-propionylpiperidine. It is usually available as the hydrochloride, which is a white powder. It is synthesized by alkylating (3-methoxyphenyl)acetonitrile with bis(2-chloroethyl)methylamine, followed by reaction with ethylmagnesium bromide, and finally O-demethylation with hydrobromic acid.[10]
Because of a strong vesicant nature of bis(2-chloroethyl)methylamine there are many other routes developed for obtaining ketobemidone. A route depicted below lays through first alkylating the same (3-methoxyphenyl)acetonitrile with 2-chloro-N,N-dimethylethylamine or 2-chloro-N-benzyl-N-methylethylamine.[11] Next, those amines are alkylated once again using a mixed 1-bromo-2-chloroethane, thus completing the piperidine ring and obtaining a quaternary ammonium salt, which can be dequaternized using thiophenol salt[12] (for N,N-dimethylammonium) or catalytic hydrogenation[13] (for both compounds) to a common 4-(3-methoxyphenyl)-4-cyano-1-methyl-pyperidine. The later yields ketobemidone after Grignard reaction with ethylmagnesium bromide and ether cleavage.
References
- Ebert, B; Thorkildsen, C; Andersen, S; Christrup, LL; Hjeds, H (1 September 1998). "Opioid analgesics as noncompetitive N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) antagonists". Biochemical Pharmacology. 56 (5): 553–9. doi:10.1016/S0006-2952(98)00088-4. PMID 9783723.
- Brayfield, A, ed. (9 January 2017). "Ketobemidone Hydrochloride: Martindale: The Complete Drug Reference". MedicinesComplete. London, UK: Pharmaceutical Press. Retrieved 6 September 2017.
- GB patent 609763, "Manufacture of piperidyl ketones", published 1948-10-06, assigned to Ciba Ltd.
- US patent 2486796, Meischer, K.; Kaegi, H., "Esters of 1-alkyl-4-hydroxyphenyl-piperidil-4-ketones", issued 1949-11-01
- "DEA Diversion Control Division".
- "Development of Synthetic Narcotic Drugs". Bulletin on Narcotic Drugs. 1956 (1): 11–14. 1956. Retrieved 2012-07-05.
- Bondesson, U. (1982). Biological Fate of Ketobemidone in Man. Abstracts of Uppsala Dissertations from the Faculty of Pharmacy. 68. ISBN 978-91-554-1243-2.
- "Statistical Information on Narcotic Drugs" (PDF). INCB. 2004. Retrieved 2006-09-07.
- Bondesson, U.; Hartvig, P.; Danielsson, B. (1981). "Quantitative Determination of the Urinary Excretion of Ketobemidone and four of its Metabolites after Intravenous and Oral Administration in Man". Drug Metabolism and Disposition. 9 (4): 376–380. PMID 6114838.
- William Andrew Publishing (2013). "Cetobemidone" (excerpt). Pharmaceutical Manufacturing Encyclopedia. Elsevier. ISBN 9780815518563.
- Avison, A. W. D.; Morrison, A. L. (1950). "303. Synthetic Analgesics. Part VI. The Synthesis of Ketobemidone". Journal of the Chemical Society (Resumed). 1950: 1469–1471. doi:10.1039/JR9500001469.
- Shamma, Maurice; Deno, Norman C; Remar, Joseph F (1966). "The selective demethylation of quaternary ammonium salts". Tetrahedron Letters. 7 (13): 1375–1379. doi:10.1016/s0040-4039(01)99725-4.
- Kägi, H; Miescher, K (1949). "Über eine neue Synthese morphinähnlich wirkender 4-Phenylpiperidin-4-alkylketone und verwandter Verbindungen". Helvetica Chimica Acta. 32 (7): 2489–2507. doi:10.1002/hlca.19490320736.