Tynorphin
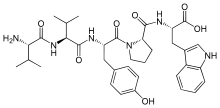
Tynorphin is a synthetic opioid peptide which is a potent and competitive inhibitor of the enkephalinase class of enzymes which break down the endogenous enkephalin peptides.[1] It specifically inactivates dipeptidyl aminopeptidase III (DPP3) with very high efficacy, but also inhibits neutral endopeptidase (NEP), aminopeptidase N (APN), and angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) to a lesser extent.[1] It has a pentapeptide structure with the amino acid sequence Val-Val-Tyr-Pro-Trp.
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C35H46N6O7 |
| Molar mass | 662.8 g/mol g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
Tynorphin was discovered in an attempt to develop an enkephalinase inhibitor of greater potency than spinorphin.[1]
See also
References
- Yamamoto Y, Hashimoto J, Shimamura M, Yamaguchi T, Hazato T (April 2000). "Characterization of tynorphin, a potent endogenous inhibitor of dipeptidyl peptidaseIII". Peptides. 21 (4): 503–8. doi:10.1016/S0196-9781(00)00174-1. PMID 10822105.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative
Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.