17α-Estradiol
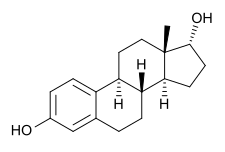
17α-Estradiol (also known as 17α-E2, 17-epiestradiol, alfatradiol, or estra-1,3,5(10)-triene-3,17α-diol) is a minor and weak endogenous steroidal estrogen that is related to 17β-estradiol (better known simply as estradiol).[2] It is the C17 epimer of estradiol.[2] It has approximately 100-fold lower estrogenic potency than 17β-estradiol.[3] The compound shows preferential affinity for the ERα over the ERβ.[2][4] Although 17α-estradiol is far weaker than 17β-estradiol as an agonist of the nuclear estrogen receptors, it has been found to bind to and activate the brain-expressed ER-X with a greater potency than that of 17β-estradiol, suggesting that it may be the predominant endogenous ligand for the receptor.[5]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(8R,9S,13S,14S,17R)-13-Methyl-6,7,8,9,11,12,14,15,16,17-decahydrocyclopenta[a]phenanthrene-3,17-diol | |
| Other names
17α-E2; Alpha-Estradiol; Alfatradiol; 17-Epiestradiol; Estra-1,3,5(10)-triene-3,17α-diol; β-Estradiol (obsolete, misleading)[1] | |
| Identifiers | |
CAS Number |
|
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.322 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
Chemical formula |
C18H24O2 |
| Molar mass | 272.388 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
See also
References
- J. Elks (14 November 2014). The Dictionary of Drugs: Chemical Data: Chemical Data, Structures and Bibliographies. Springer. pp. 897–. ISBN 978-1-4757-2085-3.
- Zhu BT, Han GZ, Shim JY, Wen Y, Jiang XR (2006). "Quantitative structure-activity relationship of various endogenous estrogen metabolites for human estrogen receptor alpha and beta subtypes: Insights into the structural determinants favoring a differential subtype binding". Endocrinology. 147 (9): 4132–50. doi:10.1210/en.2006-0113. PMID 16728493.
- Ralph M. Trüeb; Won-Soo Lee (13 February 2014). Male Alopecia: Guide to Successful Management. Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 93–. ISBN 978-3-319-03233-7.
- Kuiper GG, Carlsson B, Grandien K, Enmark E, Häggblad J, Nilsson S, Gustafsson JA (1997). "Comparison of the ligand binding specificity and transcript tissue distribution of estrogen receptors alpha and beta". Endocrinology. 138 (3): 863–70. doi:10.1210/endo.138.3.4979. PMID 9048584.
- Toran-Allerand CD, Tinnikov AA, Singh RJ, Nethrapalli IS (2005). "17alpha-estradiol: a brain-active estrogen?". Endocrinology. 146 (9): 3843–50. doi:10.1210/en.2004-1616. PMID 15947006.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative
Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.