Becampanel
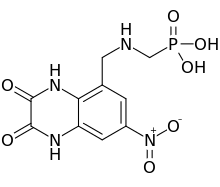
Becampanel (INN) (code name AMP397) is a quinoxalinedione derivative drug which acts as a competitive antagonist of the AMPA receptor (IC50 = 11 nM).[1][2][3][4] It was investigated as an anticonvulsant for the treatment of epilepsy by Novartis, and was also looked at as a potential treatment for neuropathic pain and cerebral ischemia, but never completed clinical trials.[1][2][3][5]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C10H11N4O7P |
| Molar mass | 330.191 g/mol g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
References
- John B. Taylor; D. J. Triggle (2007). Comprehensive medicinal chemistry II. Elsevier. p. 290. ISBN 978-0-08-044513-7.
- Kwan P, Brodie MJ (September 2007). "Emerging drugs for epilepsy". Expert Opin Emerg Drugs. 12 (3): 407–22. doi:10.1517/14728214.12.3.407. PMID 17874969.
- Citraro R, Aiello R, Franco V, De Sarro G, Russo E (March 2014). "Targeting α-amino-3-hydroxyl-5-methyl-4-isoxazole-propionate receptors in epilepsy". Expert Opin. Ther. Targets. 18 (3): 319–34. doi:10.1517/14728222.2014.874416. PMID 24387310.
- World Health Organization (1988). International Nonproprietary Names (INN) for Pharmaceutical Substances. W.H.O. ISBN 9789240560369.
- Pathan SA, Jain GK, Akhter S, Vohora D, Ahmad FJ, Khar RK (September 2010). "Insights into the novel three 'D's of epilepsy treatment: drugs, delivery systems and devices". Drug Discov. Today. 15 (17–18): 717–32. doi:10.1016/j.drudis.2010.06.014. PMID 20603226.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative
Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.