Putrescine
Putrescine is a foul-smelling[1] organic chemical compound NH2(CH2)4NH2 (1,4-diaminobutane or butanediamine) that is related to cadaverine; both are produced by the breakdown of amino acids in living and dead organisms and both are toxic in large doses.[2][3] The two compounds are largely responsible for the foul odor of putrefying flesh, but also contribute to the odor of such processes as bad breath and bacterial vaginosis.[4] They are also found in semen and some microalgae, together with related molecules like spermine and spermidine.
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Butane-1,4-diamine | |
| Other names
1,4-Diaminobutane, 1,4-Butanediamine | |
| Identifiers | |
CAS Number |
|
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| 3DMet | |
Beilstein Reference |
605282 |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.003.440 |
| EC Number |
|
Gmelin Reference |
1715 |
| KEGG | |
| MeSH | Putrescine |
PubChem CID |
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UN number | 2928 |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
Chemical formula |
C4H12N2 |
| Molar mass | 88.154 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Colourless crystals |
| Odor | strong, piperidine-like |
| Density | 0.877 g/mL |
| Melting point | 27.5 °C (81.5 °F; 300.6 K) |
| Boiling point | 158.6 °C; 317.4 °F; 431.7 K |
Solubility in water |
Miscible |
| log P | −0.466 |
| Vapor pressure | 2.33 mm Hg at 25 deg C (est) |
Henry's law constant (kH) |
3.54x10−10 atm-cu m/mol at 25 deg C (est) |
Refractive index (nD) |
1.457 |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms |    |
| GHS Signal word | Danger |
GHS hazard statements |
H228, H302, H312, H314, H331 |
GHS precautionary statements |
P210, P261, P280, P305+351+338, P310 |
| Flash point | 51 °C (124 °F; 324 K) |
| Explosive limits | 0.98–9.08% |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LD50 (median dose) |
|
| Related compounds | |
Related alkanamines |
|
Related compounds |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
History
Putrescine[5] and cadaverine[6] were first described in 1885 by the Berlin physician Ludwig Brieger (1849–1919).[7]
Receptors
In humans, molecular modelling and docking experiments have shown that putrescine fits into the binding pocket of the human TAAR6 and TAAR8 receptors.[8]
Production
Putrescine is produced on an industrial scale by hydrogenation of succinonitrile, which is produced by addition of hydrogen cyanide to acrylonitrile.[9] Putrescine is reacted with adipic acid to yield the polyamide Nylon 46, which is marketed by DSM under the trade name Stanyl.[10] Biotechnological production of putrescine from renewable feedstock is a promising alternative to the chemical synthesis. A metabolically engineered strain of Escherichia coli that produces putrescine at high titer in glucose mineral salts medium has been described.[11]
Biochemistry
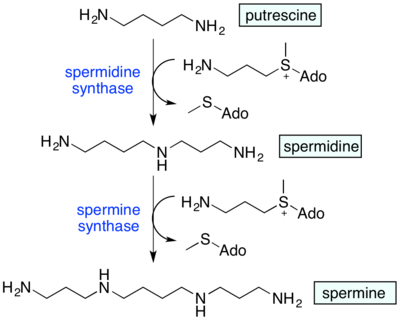
Spermidine synthase uses putrescine and S-adenosylmethioninamine (decarboxylated S-adenosyl methionine) to produce spermidine. Spermidine in turn is combined with another S-adenosylmethioninamine and gets converted to spermine.
Putrescine is synthesized in small quantities by healthy living cells by the action of ornithine decarboxylase.
Putrescine is synthesized biologically via two different pathways, both starting from arginine.
- In one pathway, arginine is converted into agmatine, with a reaction catalyzed by the enzyme arginine decarboxylase (ADC); then agmatine is transformed into N-carbamoylputrescine by agmatine imino hydroxylase (AIH). Finally, N-carbamoylputrescine is converted into putrescine.[12]
- In the second pathway, arginine is converted into ornithine and then ornithine is converted into putrescine by ornithine decarboxylase (ODC).
The polyamines, of which putrescine is one of the simplest, appear to be growth factors necessary for cell division.
Toxicity
Putrescine is toxic in large doses. In rats it has a low acute oral toxicity of 2000 mg/kg body weight, with no-observed-adverse-effect level of 2000 ppm (180 mg/kg body weight/day).[13]
When heated to decomposition, putrescine emits toxic fumes of NOx.[14]
See also
- Skatole
- Trimethylamine
References
- Haglund, William (1996). Forensic taphonomy: The Postmortem Fate of Human Remains. CRC Press. pp. 100. ISBN 0-8493-9434-1.
- Lewis, Robert Alan (1998). Lewis' Dictionary of Toxicology. CRC Press. pp. 212. ISBN 1-56670-223-2.
- Kamhi, Ellen, Ph.D., RN, HNC (2007). Alternative Medicine Magazine's Definitive Guide to Weight Loss. Celestial Arts. p. 14. ISBN 1-58761-259-3.
Ornithine is converted by bowel bacteria into a toxic substance called putrescine, which in turn degrades into polyamines, such as spermadine, spermine, and cadaverine (literally meaning "the essence of dead cadavers").
- Yeoman, CJ;Thomas, SM; Miller, ME; Ulanov, AV; Torralba, M; Lucas, S; Gillis, M; Cregger, M; Gomez, A; Ho, M; Leigh, SR; Stumpf, R; Creedon, DJ; Smith, MA; Weisbaum, JS; Nelson, KE; Wilson, BA; White, BA (2013). "A multi-omic systems-based approach reveals metabolic markers of bacterial vaginosis and insight into the disease". PLOS ONE. 8 (2): e56111. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0056111. PMC 3566083. PMID 23405259.CS1 maint: uses authors parameter (link)
- Ludwig Brieger, "Weitere Untersuchungen über Ptomaine" [Further investigations into ptomaines] (Berlin, Germany: August Hirschwald, 1885), page 43. From page 43: Ich nenne dasselbe Putrescin, von putresco, faul werden, vermodern, verwesen. (I call this [compound] "putrescine", from [the Latin word] putresco, to become rotten, decay, rot.)
- Ludwig Brieger, "Weitere Untersuchungen über Ptomaine" [Further investigations into ptomaines] (Berlin, Germany: August Hirschwald, 1885), page 39.
- Brief biography of Ludwig Brieger (in German). Biography of Ludwig Brieger in English.
- Izquierdo, C; Gomez-Tamayo, JC; Nebel, J-C; Pardo, L; Gonzalez, A (2018). "Identifying human diamine sensors for death related putrescine and cadaverine molecules". PLOS Computational Biology. 14 (1): e1005945. doi:10.1371/journal.pcbi.1005945. PMC 5783396.
- "Nitriles". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry (7th ed.). Retrieved 2007-09-10.
- "Electronic Control Modules (ECU) - Electrical & Electronics - Applications - DSM". Dsm.com. Retrieved 18 December 2015.
- "Metabolic Engineering of Escherichia coli for the Production of Putrescine: A Four Carbon Diamine". Archived from the original on 2013-01-05. Retrieved 2010-06-10.
- Srivenugopal KS, Adiga PR (September 1981). "Enzymic conversion of agmatine to putrescine in Lathyrus sativus seedlings. Purification and properties of a multifunctional enzyme (putrescine synthase)". J. Biol. Chem. 256 (18): 9532–41. PMID 6895223.
- Til, H.P.; Falke, H.E.; Prinsen, M.K.; Willems, M.I. (1997). "Acute and subacute toxicity of tyramine, spermidine, spermine, putrescine and cadaverine in rats". Food and Chemical Toxicology. 35 (3–4): 337–348. doi:10.1016/S0278-6915(97)00121-X. ISSN 0278-6915.
- "Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB).” U.S. National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.