BMS-470539
BMS-470539 is a small-molecule experimental drug which acts as a potent and highly selective full agonist of the MC1 receptor.[1][2] It was discovered in 2003 as part of an effort to understand the role of the MC1 receptor in immunomodulation, and has since been used in scientific research to determine its role in inflammatory processes.[1][2][3] The compound was designed with the intention of mimicking the central His-Phe-Arg-Trp pharmacophore of the melanocortins,[1][2] and this proved to be successful based on its favorable pharmacodynamic profile.
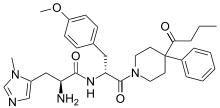 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Routes of administration | S.C.[1] |
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 100% (with S.C. administration)[1] |
| Elimination half-life | 1.7 hours[1] |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| ChemSpider | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C32H41N5O4 |
| Molar mass | 559.70 g/mol g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| | |
See also
- Afamelanotide
- Bremelanotide
- Melanotan II
- Modimelanotide
- Setmelanotide
References
- Kang L, McIntyre KW, Gillooly KM, et al. (October 2006). "A selective small molecule agonist of the melanocortin-1 receptor inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced cytokine accumulation and leukocyte infiltration in mice". Journal of Leukocyte Biology. 80 (4): 897–904. doi:10.1189/jlb.1204748. PMID 16888084.
- Herpin TF, Yu G, Carlson KE, et al. (March 2003). "Discovery of tyrosine-based potent and selective melanocortin-1 receptor small-molecule agonists with anti-inflammatory properties". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 46 (7): 1123–6. doi:10.1021/jm025600i. PMID 12646021.
- Leoni G, Voisin MB, Carlson K, Getting S, Nourshargh S, Perretti M (May 2010). "The melanocortin MC(1) receptor agonist BMS-470539 inhibits leucocyte trafficking in the inflamed vasculature". British Journal of Pharmacology. 160 (1): 171–80. doi:10.1111/j.1476-5381.2010.00688.x. PMC 2860217. PMID 20331604.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative
Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.