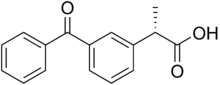
Dexketoprofen
Dexketoprofen is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID). It is manufactured by Menarini, under the tradename Keral. It is available in the UK, as dexketoprofen trometamol, as a prescription-only drug and in Latin America as Enantyum, produced by Menarini. Also, in Italy and Spain it is available as an over-the-counter drug (OTC) under the trade name Enantyum. In Latvia, Lithuania and Estonia it is available as an OTC under the tradename Dolmen [1] In Mexico it is available in tablet form as "Stadium" made by Menarini. It is the dextrorotatory stereoisomer of ketoprofen.[2]
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.118.639 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C16H14O3 |
| Molar mass | 254.28056 g/mol g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| | |
Medical uses
Short-term treatment of mild to moderate pain, including dysmenorrhoea. It is also used for migraines and knee pain.
Side effects
It may cause dizziness, and patients should not, therefore, drive or operate heavy machinery or vehicles until they are familiar with how dexketoprofen affects them. Concomitant use of alcohol and other sedatives may potentiate this effect. In a small subset of individuals the dizziness may be intolerable and require transition to an alternative treatment.
Pharmacology
Dexketoprofen belongs to a class of medicines called NSAIDs. It works by blocking the action of a substance in the body called cyclo-oxygenase, which is involved in the production of chemicals in the body called prostaglandins. Prostaglandins are produced in response to injury or certain diseases and would otherwise go on to cause swelling, inflammation and pain. By blocking cyclo-oxygenase, dexketoprofen prevents the production of prostaglandins and therefore reduces inflammation and pain. Along with peripheral analgesic action, it possesses central analgesic action.
References
- "Medicinal products authorised in Estonia". State Agency of Medicine. 22 May 2014. Retrieved 23 May 2014.
- "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2016-08-12. Retrieved 2016-07-05.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)