Ertapenem
Ertapenem is a carbapenem antibiotic marketed by Merck as Invanz.[1]
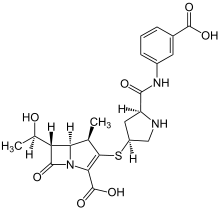 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Invanz |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| License data | |
| Pregnancy category | |
| Routes of administration | Intramuscular, intravenous |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 90% (intramuscular) |
| Protein binding | Inversely proportional to concentration; 85 to 95% |
| Metabolism | Minor hydrolysis of beta-lactam ring, CYP not involved |
| Elimination half-life | 4 hours |
| Excretion | Renal (80%) and fecal (10%) |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C22H25N3O7S |
| Molar mass | 475.516 g/mol g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| | |
References
- Papp-Wallace KM, Endimiani A, Taracila MA, Bonomo RA (November 2011). "Carbapenems: past, present, and future". Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 55 (11): 4943–60. doi:10.1128/AAC.00296-11. PMC 3195018. PMID 21859938.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative
Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.