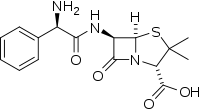
Aminopenicillin
The aminopenicillins are a group of antibiotics in the penicillin family that are structural analogs of ampicillin (which is the 2-amino derivative of benzylpenicillin, hence the name).[1] Like other penicillins and beta-lactam antibiotics, they contain a beta-lactam ring that is crucial to its antibacterial activity.
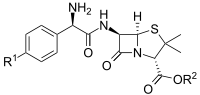
Generalized structure of aminopenicillins
Aminopenicillins feature a positively charged amino group that enhances their uptake through bacterial porin channels. This does not, however, prevent resistance conferred by bacterial beta-lactamases.[2] Members of this family include ampicillin, amoxicillin and bacampicillin.[3]
References
- Cunha BA (August 1992). "Aminopenicillins in urology". Urology. 40 (2): 186–90. doi:10.1016/0090-4295(92)90525-2. PMID 1502761.
- Golan, David E. (2011-12-15). Principles of Pharmacology. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. ISBN 9781608312702.
- "Mayo Clinic Proceedings". Retrieved 2008-12-26.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative
Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.