Cefpodoxime
Cefpodoxime is an oral, third-generation cephalosporin antibiotic. It is active against most Gram-positive and Gram-negative organisms. Notable exceptions include Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Enterococcus, and Bacteroides fragilis. Currently, it is only marketed as generic preparations in the US, according to the FDA Orange Book. It is commonly used to treat acute otitis media, pharyngitis, sinusitis, and gonorrhea. It also finds use as oral continuation therapy when intravenous cephalosporins (such as ceftriaxone) are no longer necessary for continued treatment.
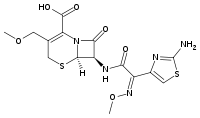 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Vantin, others |
| Other names | Cefprodoxime proxetil |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a698024 |
| Pregnancy category | |
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 50% |
| Protein binding | 21% to 29% |
| Metabolism | Negligible. Cefpodoxime proxetil is metabolized to cefpodoxime by the liver |
| Elimination half-life | 2 hours |
| Excretion | Renal, unchanged |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.210.871 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C15H17N5O6S2 |
| Molar mass | 427.458 g/mol g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| | |
Cefpodoxime inhibits cell wall synthesis by inhibiting the final transpeptidation step of peptidoglycan synthesis in cell walls. It has well established pharmacokinetic profile with absorption of 50%. It is indicated in community acquired pneumonia, uncomplicated skin and skin structure infections, and uncomplicated urinary tract infections.
It was patented in 1980 and approved for medical use in 1989.[1]
Spectrum of bacterial susceptibility and resistance
Cefpodoxime has been used to fight pathogenic bacteria responsible for causing gonorrhoea, tonsillitis, pneumonia, and bronchitis. Representative pathogenic genera include Streptococcus, Haemophilus, and Neisseria. The following represents MIC susceptibility data for a few medically significant microorganisms.
- Haemophilus influenzae: ≤0.03 - 1 μg/ml
- Neisseria gonorrhoeae: 0.004 - 0.06 μg/ml
- Streptococcus pyogenes: ≤0.004 - 2 μg/ml
Brand name
Zoetis markets cefpodoxime proxetil under the trade name Simplicef for veterinary use. The dose range in dogs is 5–10 mg/kg body weight, administered orally, once a day. Finecure,[3] India markets the products under trade name Cefpo.[4]
Vantin (by Pfizer)[5] in suspension or tablet form.
Toraxim (by Delta Pharma Ltd. Bangladesh)
Trucef (by Renata Limited, Bangladesh)
Orelox (by Sanofi-Aventis)[6]
MAPDOX-CV: Cefpodoxime and Clavulanic acid combination
MONOTAX O (Cefpodoxime)/ MONOTAX CV (Cefpodoxime and Clavulanic acid combination) (by Zydus Healthcare Ltd.)
References
- Fischer, Jnos; Ganellin, C. Robin (2006). Analogue-based Drug Discovery. John Wiley & Sons. p. 495. ISBN 9783527607495.
- http://www.toku-e.com/Assets/MIC/Cefpodoxime%20Free%20acid.pdf
- "Pharmaceuticals Manufacturer, Marketer, Pharmaceutical Manufacturing Company India". www.finecurepharma.com. Retrieved 2019-05-26.
- "Anti Biotics and Anti Bacterial". Finecurepharmaceuticalsltd. Archived from the original on 2012-03-06. Retrieved 2012-03-27.
- "Vantin - Drugs.com". www.drugs.com. Retrieved 2019-05-02.
- "Orelox - Drugs.com". www.drugs.com. Retrieved 2015-11-28.
External links
- CID 6526396 from PubChem - cefpodoxime proxetil
- Vantin Tablets and Oral Suspension Torpod (Torrent) Full U.S. Prescribing Information (from manufacturer's website)
- Simplicef (from manufacturer's website)
- http://www.intaspharma.com/index.php?option=com_djcatalog2&view=itemstable&cid=3&Itemid=77