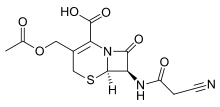
Cefacetrile
Cefacetrile (INN, also spelled cephacetrile) is a broad-spectrum first generation cephalosporin antibiotic effective in gram-positive and gram-negative bacterial infections. It is a bacteriostatic antibiotic.[1][2] Cefacetrile is marketed under the trade names Celospor, Celtol, and Cristacef,[3] and as Vetimast for the treatment of mammary infections in lactating cows.[2]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Celospor, Celtol, Cristacef |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| Routes of administration | Intravenous, intramuscular, intramammary |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Protein binding | 23 to 38% |
| Elimination half-life | 1.2 hours |
| Excretion | Renal (72%) |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.030.449 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C13H13N3O6S |
| Molar mass | 339.325 g/mol g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| (verify) | |
Synthesis
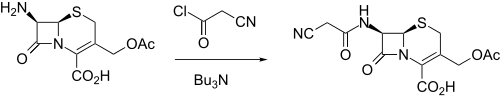
Cefacetrile synthesis: NL 6600586 (1966 to Ciba-Geigy).
It was made by reacting 7-ACA (7-aminocephalosporanic acid) with cyanoacetyl chloride in the presence of tributylamine.
References
- "Cefacetrile Summary Report" (PDF). European Medicines Agency, Committee for Veterinary Medicinal Products. 1998.
- Haberfeld, H, ed. (2007). Austria-Codex (in German) (2007/2008 ed.). Vienna: Österreichischer Apothekerverlag. ISBN 3-85200-183-8.
- Horiuchi, N.; Oyakawa, Y.; Oka, R.; Fujiwara, T. (1980). "Clinical evaluation of cephacetrile (Celtol) for respiratory infections (author's transl)". The Japanese journal of antibiotics. 33 (10): 1145–1155. PMID 7206219.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative
Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.