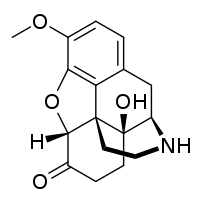
Noroxycodone
Noroxycodone is the major metabolite of the opioid analgesic oxycodone.[1][2][3] It is formed from oxycodone in the liver via N-demethylation predominantly by CYP3A4.[1][2][3] Noroxycodone binds to and activates the μ-opioid receptor (MOR) similarly to oxycodone, although with one-third of the affinity of oxycodone and 5- to 10-fold lower activational potency.[1][4][5] However, although a potent MOR agonist, noroxycodone poorly crosses the blood-brain-barrier into the central nervous system, and for this reason, is only minimally analgesic in comparison.[6][5][4][7]
 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.055.334 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C17H19NO4 |
| Molar mass | 301.342 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
References
- Howard Smith; Steven Passik (25 April 2008). Pain and Chemical Dependency. Oxford University Press, USA. pp. 195–. ISBN 978-0-19-530055-0.
- Richard A. McPherson; Matthew R. Pincus (31 March 2016). Henry's Clinical Diagnosis and Management by Laboratory Methods. Elsevier Health Sciences. pp. 336–. ISBN 978-0-323-41315-2.
- Pavel Anzenbacher; Ulrich M. Zanger (29 May 2012). Metabolism of Drugs and Other Xenobiotics. John Wiley & Sons. pp. 420–. ISBN 978-3-527-32903-8.
- Lemberg, Kim K.; Siiskonen, Antti O.; Kontinen, Vesa K.; Yli-Kauhaluoma, Jari T.; Kalso, Eija A. (2008). "Pharmacological Characterization of Noroxymorphone as a New Opioid for Spinal Analgesia". Anesthesia & Analgesia. 106 (2): 463–470. doi:10.1213/ane.0b013e3181605a15. ISSN 0003-2999. PMID 18227301.
- Victor R. Preedy (25 April 2016). Neuropathology of Drug Addictions and Substance Misuse Volume 3: General Processes and Mechanisms, Prescription Medications, Caffeine and Areca, Polydrug Misuse, Emerging Addictions and Non-Drug Addictions. Elsevier Science. pp. 462–464. ISBN 978-0-12-800677-1.
- Lalovic, B; Kharasch, E; Hoffer, C; Risler, L; Liuchen, L; Shen, D (2006). "Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of oral oxycodone in healthy human subjects: Role of circulating active metabolites". Clinical Pharmacology & Therapeutics. 79 (5): 461–479. doi:10.1016/j.clpt.2006.01.009. ISSN 0009-9236. PMID 16678548.
- Klimas, Romina; Witticke, Diana; El Fallah, Sarah; Mikus, Gerd (2013). "Contribution of oxycodone and its metabolites to the overall analgesic effect after oxycodone administration". Expert Opinion on Drug Metabolism & Toxicology. 9 (5): 517–528. doi:10.1517/17425255.2013.779669. ISSN 1742-5255.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative
Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.