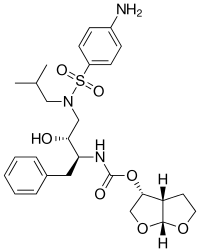
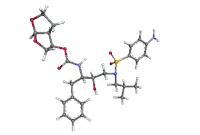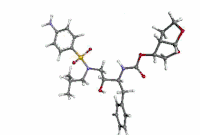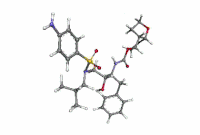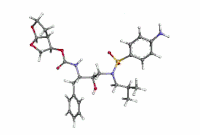
Darunavir
Darunavir (DRV), sold under the brand name Prezista among others, is an antiretroviral medication used to treat and prevent HIV/AIDS.[1] It is generally recommended for use with other antiretrovirals.[1] It is often used with low doses of ritonavir or cobicistat to increase darunavir levels.[1] It may be used for prevention after a needlestick injury or other potential exposure.[1] It is taken by mouth once to twice a day.[1]
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Prezista, Prezcobix, others[1] |
| Other names | TMC114 |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a607042 |
| License data | |
| Pregnancy category | |
| Routes of administration | by mouth |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 37% (without ritonavir), 82% (with ritonavir) |
| Protein binding | 95% |
| Metabolism | hepatic (CYP3A4) |
| Elimination half-life | 15 hours |
| Excretion | Faeces (80%), urine (14%) |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| NIAID ChemDB | |
| PDB ligand | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.111.730 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C27H37N3O7S |
| Molar mass | 547.665 g/mol g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| | |
Common side effects include diarrhea, nausea, abdominal pain, headache, and rash.[1] Severe side effects include allergic reactions, liver problems, and skin rashes such as toxic epidermal necrolysis.[1] While poorly studied in pregnancy it appears to be safe for the baby.[2] It is of the protease inhibitor (PI) class and works by blocking HIV protease.[1]
Darunavir was approved for medical use in the United States in 2006.[1] It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines, the most effective and safe medicines needed in a health system.[3]. The wholesale cost in the developing world is about US$66 per month.[4] In the United States it costs more than $200 per month.[5] The combination darunavir/cobicistat is available as a single pill.[6]
Medical uses
Darunavir is an OARAC (DHHS) recommended treatment option for adults and adolescents, regardless of whether they have received HIV treatment in the past.[7] In a study of patients that had never received HIV treatment, darunavir was as effective as lopinavir/ritonavir at 96 weeks with a once-daily dosing.[8] It was approved by the FDA on October 21, 2008 for people not previously treated for HIV.[9] As with other antiretrovirals, darunavir does not cure HIV/AIDS.[10]
Adverse effects
Darunavir is generally well tolerated by people. Rash is the most common side effect (7% of patients).[10] Other common side effects are diarrhea (2.3%), headache (3.8%), abdominal pain (2.3%), constipation (2.3%), and vomiting (1.5%).[10] Darunavir can also cause allergic reactions, and people allergic to ritonavir can also have a reaction to darunavir.[10]
High blood sugar, diabetes or worsening of diabetes, muscle pain, tenderness or weakness, and increased bleeding in people with hemophilia have been reported in patients taking protease inhibitor medicines like darunavir.[10] Changes in body fat have been seen in some patients taking medicines for HIV, including loss of fat from legs, arms and face, increased fat in the abdomen and other internal organs, breast enlargement, and fatty lumps on the back of the neck. The cause and long-term health effects of these conditions are not known.[10]
Drug interactions
Darunavir may interact with medications commonly taken by people with HIV/AIDS such as other antiretrovirals, and antacids such as proton pump inhibitors and H2 receptor antagonists.[10] St. John's wort may reduce the effectiveness of darunavir by increasing the breakdown of darunavir by the metabolic enzyme CYP3A.[10]
Mechanism of action
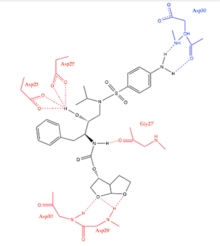
Darunavir is a nonpeptidic inhibitor of protease (PR) that lodges itself in the active site of PR through a number of hydrogen bonds.[11] It was developed to increase interactions with HIV-1 protease and to be more resistant against HIV-1 protease mutations. With a Kd (dissociation constant) of 4.5 x 10−12 M, darunavir has a much stronger interaction with PR and its dissociation constant is 1/100 to 1/1000 of other protease inhibitors.[12] This strong interaction comes from increased hydrogen bonds between darunavir and the backbone of the PR active site (Figure 2). Darunavir's structure allows it to create more hydrogen bonds with the PR active site than most PIs that have been developed and approved by the FDA.[13] Furthermore, the backbone of HIV-1 protease maintains its spatial conformation in the presence of mutations.[14] Because darunavir interacts with this stable portion of the protease, the PR-PI interaction is less likely to be disrupted by a mutation.[13]
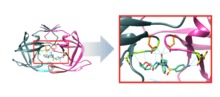
Catalytic site
The chemical activity of the HIV-1 protease depends on two residues in the active site, Asp25 and Asp25’, one from each copy of the homodimer.[15] Darunavir interacts with these catalytic aspartates and the backbone of the active site through hydrogen bonds, specifically binding to residues Asp25, Asp25’, Asp 29, Asp 30, Asp 30’, and Gly 27 (Figure 3). This interaction prevents viral replication, as it competitively inhibits the viral polypeptides from gaining access to the active site and strongly binds to the enzymatic portions of this protein.[11]
Cost
In the US and UK, healthcare costs were estimated to be lower with boosted darunavir than with investigator-selected control protease inhibitors in treatment-experienced patients.
History
Darunavir was developed by Tibotec, and was named after Arun K. Ghosh, who discovered the molecule at the University of Illinois at Chicago.[17] It was approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) on June 23, 2006.[18][19]
The development of first-generation clinical inhibitors was founded on creating more protease-ligand interactions through hydrogen bonding and hydrophobic interactions.[11] The first HIV protease inhibitor approved by the FDA was saquinavir, which was designed to target wild-type HIV-1 protease.[20] However, this inhibitor is no longer effective due to resistance-causing mutations on the HIV-1 protease structure. The HIV genome has high plasticity, so has been able to become resistant to multiple HIV-1 protease inhibitors.[21] Since saquinavir, the FDA has approved several PIs, including darunavir.[22] Darunavir was granted approval by the FDA on June 23, 2006.[22]
See also
References
- "Darunavir". The American Society of Health-System Pharmacists. Archived from the original on 10 November 2016. Retrieved 28 November 2016.
- "Darunavir (Prezista) Use During Pregnancy". www.drugs.com. Archived from the original on 20 December 2016. Retrieved 4 December 2016.
- "WHO Model List of Essential Medicines (19th List)" (PDF). World Health Organization. April 2015. Archived (PDF) from the original on 13 December 2016. Retrieved 8 December 2016.
- "Darunavir". International Drug Price Indicator Guide. Retrieved 28 November 2016.
- Hamilton, Richart (2015). Tarascon Pocket Pharmacopoeia 2015 Deluxe Lab-Coat Edition. Jones & Bartlett Learning. p. 69. ISBN 9781284057560.
- "Darunavir / Cobicistat". AIDSinfo. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services.
- Guidelines for the Use of Antiretroviral Agents in HIV-1-Infected Adults and Adolescents, November 3, 2008, Developed by the DHHS Panel on Antiretroviral Guidelines for Adults and Adolescents – A Working Group of the Office of AIDS Research Advisory Council (OARAC). full guidelines Archived 2009-01-13 at the Wayback Machine.
- hivandhepatitis.com Archived 2007-07-13 at the Wayback Machine, Efficacy and Safety of Boosted Darunavir (Prezista) Are Superior to Lopinavir/ritonavir (Kaletra) at 96 Weeks: ARTEMIS Trial, 2008-10-28, URL Archived 2009-07-19 at the Wayback Machine.
- hivandhepatitis.com Archived 2007-07-13 at the Wayback Machine, Darunavir (Prezista) Receives Full Traditional Approval, Dose Set for Treatment-naive Patients, Caution Urged for Pregnant Women, 2008-10-24, URL Archived 2009-05-19 at the Wayback Machine.
- "Drug Monograph, Prezista". Archived from the original on 2016-11-11.
- Leonis, G.; Czyznikowska, Z.; et al. (2012). "Computational Studies of Darunavir into HIV-1 Protease and DMPC Bilayer: Necessary Conditions for Effective Binding and the Role of the Flaps". J. Chem. Inf. Model. 52: 1542–1558. doi:10.1021/ci300014z.
- King, N. M.; Prabu-Jeyabalan, M.; et al. (2004). "Structural and Thermodynamic Basis for the Binding of TMC114, a Next-Generation Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 Protease Inhibitor". Journal of Virology. 78: 21.
- Lefebvre, E.; Schiffer, C. A. (2008). "Resilience to Resistance of HIV-1 Protease Inhibitors: Profile of Darunavir". AIDS Rev. 10 (3): 131–142.
- Lascar, R. M.; Benn, P. (2009). "Role of darunavir in the management of HIV infection". HIV AIDS (Auckl). 1: 31–39.
- Li, D.; Zhang, Y.; et al. (2014). "Investigation on the mechanism for the binding and drug resistance of wild type and mutations of G86 residue in HIV-1 protease complexed with Darunavir by molecular dynamic simulation and free energy calculation". J. Molecular Modeling. 20: 2122. doi:10.1007/s00894-014-2122-y.
- "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2007-07-04. Retrieved 2007-06-30.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- "Darunavir: promising initial results". The Lancet. 369: 1143–1144. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(07)60499-1.
- "2006 - FDA Approves New HIV Treatment for Patients Who Do Not Respond to Existing Drugs". www.fda.gov. Archived from the original on 2016-11-13. Retrieved 2016-11-10.
- Liu, F.; Kovalevsky, A.Y. (2008). "Effect of Flap Mutations on Structure of HIV-1 Protease and Inhibition by Saquinavir and Darunavir". J. Mol. Biol. 381 (1): 102–115. doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2008.05.062. PMC 2754059.
- Eron, J (2000). "HIV-1 Protease Inhibitors". Oxford Journal of Clinical Infectious Diseases. 30: 160–170.
- "HIV/AIDS Historical Time Line 2000-2010" FDA. 2011.
External links
- Darunavir FAQ at AIDSmeds.com
- Drug information in PDF