Tiabendazole
Tiabendazole (INN, BAN), also known as thiabendazole (AAN, USAN) or TBZ and the trade names Mintezol, Tresaderm, and Arbotect, is a preservative,[1] an antifungal agent, and an antiparasitic agent.
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Mintezol, others |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | By mouth, topical |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | Сmax 1–2 hours (oral administration) |
| Metabolism | GI tract |
| Elimination half-life | 8 hours |
| Excretion | Urine (90%) |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| NIAID ChemDB | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.005.206 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C10H7N3S |
| Molar mass | 201.249 g/mol g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Density | 1.103 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 293 to 305 °C (559 to 581 °F) |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| | |
Uses
Preservative
Tiabendazole is used primarily to control mold, blight, and other fungal diseases in fruits (e.g. oranges) and vegetables; it is also used as a prophylactic treatment for Dutch elm disease.
Tiabendazole is also used as a food additive,[2][3] a preservative with E number E233 (INS number 233). For example, it is applied to bananas to ensure freshness, and is a common ingredient in the waxes applied to the skins of citrus fruits. It is not approved as a food additive in the EU,[4] Australia and New Zealand.[5]
Use in treatment of aspergillosis has been reported.[6]
It is also used in anti-fungal wallboards as a mixture with azoxystrobin.
Parasiticide
As an antiparasitic, tiabendazole is able to control roundworms (such as those causing strongyloidiasis),[7] hookworms, and other helminth species which infect wild animals, livestock, and humans.[8]
Research
Genes responsible for the maintenance of cell walls in yeast have been shown to be responsible for angiogenesis in vertebrates. Tiabendazole serves to block angiogenesis in both frog embryos and human cells. It has also been shown to serve as a vascular disrupting agent to reduce newly established blood vessels. Tiabendazole has been shown to effectively do this in certain cancer cells.[9]
Pharmacodynamics
Tiabendazole works by inhibition of the mitochondrial, helminth-specific enzyme, fumarate reductase, with possible interaction with endogenous quinone.[10]
Safety
The substance appears to have a slight toxicity in higher doses, with effects such as liver and intestinal disorders at high exposure in test animals (just below LD50 level). Some reproductive disorders and decreasing weaning weight have been observed, also at high exposure. Effects on humans from use as a drug include nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite, diarrhea, dizziness, drowsiness, or headache; very rarely also ringing in the ears, vision changes, stomach pain, yellowing eyes and skin, dark urine, fever, fatigue, increased thirst and change in the amount of urine occur. Carcinogenic effects have been shown at higher doses.[11]
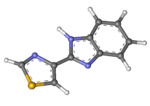
Synthesis
Intermediate arylamidine 2 is prepared by aluminium trichloride-catalyzed addition of aniline to the nitrile of 4-cyanothiazole (1).[12][13] The amidine (2) is then converted to its N-chloro derivative 3 with sodium hypochlorite (NaOCl). Upon treatment with base, this undergoes a nitrene insertion reaction (4) to produce tiabendazole (5).
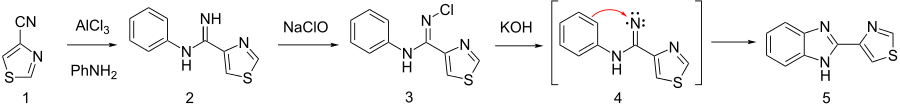
An alternative synthesis involves reacting 4-thiazolecarboxamide with o-phenylenediamine in polyphosphoric acid.[14]
Derivatives
A number of derivatives of tiabendazole are also pharmaceutical drugs, including albendazole, cambendazole, fenbendazole, oxfendazole, mebendazole, and flubendazole.
See also
- Fungicide use in the United States
- List of fungicides
References
- "E233 : E Number : Preservative". www.ivyroses.com. Retrieved 2018-08-28.
- Rosenblum, C (March 1977). "Non-Drug-Related Residues in Tracer Studies". Journal of Toxicology and Environmental Health. 2 (4): 803–14. doi:10.1080/15287397709529480. PMID 853540.
- Sax, N.I. Dangerous Properties of Industrial Materials. Vol 1-3 7th ed. New York, NY: Van Nostrand Reinhold, 1989., p. 3251
- UK Food Standards Agency: "Current EU approved additives and their E Numbers". Retrieved 2011-10-27.
- Australia New Zealand Food Standards Code"Standard 1.2.4 – Labelling of ingredients". Retrieved 2011-10-27.
- Upadhyay MP, West EP, Sharma AP (January 1980). "Keratitis due to Aspergillus flavus successfully treated with thiabendazole". Br J Ophthalmol. 64 (1): 30–2. doi:10.1136/bjo.64.1.30. PMC 1039343. PMID 6766732.
- Igual-Adell R, Oltra-Alcaraz C, Soler-Company E, Sánchez-Sánchez P, Matogo-Oyana J, Rodríguez-Calabuig D (December 2004). "Efficacy and safety of ivermectin and thiabendazole in the treatment of strongyloidiasis". Expert Opin Pharmacother. 5 (12): 2615–9. doi:10.1517/14656566.5.12.2615. PMID 15571478. Archived from the original on 2016-03-06.
- Portugal R, Schaffel R, Almeida L, Spector N, Nucci M (June 2002). "Thiabendazole for the prophylaxis of strongyloidiasis in immunosuppressed patients with hematological diseases: a randomized double-blind placebo-controlled study". Haematologica. 87 (6): 663–4. PMID 12031927.
- Cha, HJ; Byrom M; Mead PE; Ellington AD; Wallingford JB; et al. (August 2012). "Evolutionarily Repurposed Networks Reveal the Well-Known Antifungal Drug Thiabendazole to Be a Novel Vascular Disrupting Agent". PLoS Biology. 10 (8): e1001379. doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.1001379. PMC 3423972. PMID 22927795. Retrieved 2012-08-21.
- Gilman, A.G.; T.W. Rall; A.S. Nies; P. Taylor, eds. (1990). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics (8th ed.). New York, NY: Pergamon Press. p. 970.
- "Reregistration Eligibility Decision Thiabendazole" (PDF). Environmental Protection Agency. Retrieved 8 January 2013.
- Setzinger, Meyer; Painfield, North; Gaines, Water A.; Grenda, Victor J. (1965). "Novel Preparation of Benzimidazoles from N-Arylamidines. New Synthesis of Thiabendazole1". The Journal of Organic Chemistry. 30: 259–261. doi:10.1021/jo01012a061.
- L. H. Sarett, H. D. Brown, U.S. Patent 3,299,081 (1967 to Merck & Co.)
- Brown, H. D.; Matzuk, A. R.; Ilves, I. R.; Peterson, L. H.; Harris, S. A.; Sarett, L. H.; Egerton, J. R.; Yakstis, J. J.; Campbell, W. C.; Cuckler, A. C. (1961). "Antiparasitic Drugs. Iv. 2-(4'-Thiazolyl)-Benzimidazole, A New Anthelmintic". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 83 (7): 1764–1765. doi:10.1021/ja01468a052.
- Hoff, Fisher, ZA 6800351 (1969 to Merck & Co.), C.A. 72, 90461q (1970).
- Hoff, D. R.; Fisher, M. H.; Bochis, R. J.; Lusi, A.; Waksmunski, F.; Egerton, J. R.; Yakstis, J. J.; Cuckler, A. C.; Campbell, W. C. (1970). "A new broad-spectrum anthelmintic: 2-(4-Thiazolyl)-5-isopropoxycarbonylamino-benzimidazole". Experientia. 26 (5): 550–551. doi:10.1007/BF01898506.