Normustine
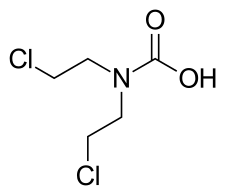
Normustine, also known as bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamic acid, is a nitrogen mustard and alkylating antineoplastic agent (i.e., chemotherapy agent).[1][2][3] It is a metabolite of a number of antineoplastic agents that have been developed for the treatment of tumors, including estramustine phosphate, alestramustine, cytestrol acetate, and ICI-85966 (stilbostat), but only the former of which has actually been marketed.[1][2][3]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamic acid |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C5H9Cl2NO2 |
| Molar mass | 186.032 g/mol g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
References
- Laurence Brunton; Bruce Chabner; Bjorn Knollman (14 January 2011). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics, Twelfth Edition. McGraw Hill Professional. p. 1709. ISBN 978-0-07-176939-6.
- Brian W. Fox; M. Fox (6 December 2012). Antitumor Drug Resistance. Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 199–. ISBN 978-3-642-69490-5.
- Michael Decker (5 April 2017). Design of Hybrid Molecules for Drug Development. Elsevier Science. pp. 201–. ISBN 978-0-08-101118-8.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative
Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.