Treosulfan
Treosulfan is a substance that is being studied in the treatment of cancer.[1] It belongs to the family of drugs called alkylating agents. It has been used mainly as a substitute of busulfan in frail patients, as the side effects and toxicity are supposedly less severe.
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | 1,2,3,4-Butanetetrol, 1,4-dimethanesulfonate, Threitol 1,4-dimethanesulfonate, Threitol 1,4-bismethanesulfonate; L-Threitol 1,4-bis(methanesulfonate); Ovastat; Threosulphan; Treosulphan; Tresulfan |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| Routes of administration | Oral, IV |
| ATC code | |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.005.529 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
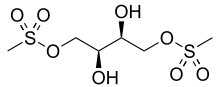
| Formula | C6H14O8S2 |
| Molar mass | 278.30056 g·mol−1 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Melting point | 101.5 to 105 °C (214.7 to 221.0 °F) |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| | |
References
- Schmittel A, Schmidt-Hieber M, Martus P, et al. (December 2006). "A randomized phase II trial of gemcitabine plus treosulfan versus treosulfan alone in patients with metastatic uveal melanoma". Ann. Oncol. 17 (12): 1826–9. doi:10.1093/annonc/mdl309. PMID 16971664.
External links
- Treosulfan entry in the public domain NCI Dictionary of Cancer Terms
![]()
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative
Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.