Mannomustine
Mannomustine (INN), also known as mannitol nitrogen mustard, tradename Degranol is an old alkylating antineoplastic agent from the group of nitrogen mustards. It was first synthesized and characterized in 1957 by Vargha et al.[1]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Degranol |
| Pregnancy category | |
| Routes of administration | Intramuscular |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Metabolism | Hepatic |
| Excretion | Renal |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number |
|
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
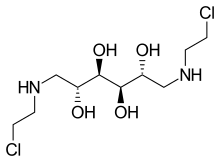
| Formula | C10H24Cl4N2O4 |
| Molar mass | 378.12 g/mol g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
The mechanism of antineoplastic activity of mannomustine, like for all other alkylating agents, lies in its ability to alkylate DNA guanine nucleobases and, thus, to prevent uncoupling of DNA strands, which is a required step for any cell to divide.
Mannomustine was, at the time of its creation as a drug, claimed to be considerably less toxic than mechlorethamine. For example, the LD50 in rats, for intravenous mannomustine administration route, is claimed to be about 56 mg/kg.[2]
See also
References
- Vargha et al., J. Chem. Soc. 1957, 805.
- Scherf et al., Arzneim.-Forsch. 20, 1467 (1970)
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative
Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.