Candidiasis
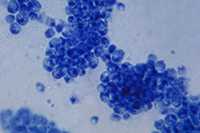
Photomicrograph of the fungus Candida albicans
Candidiasis is a fungal infection caused by yeasts that belong to the genus Candida. There are over 20 species of Candida yeasts that can cause infection in humans, the most common of which is Candida albicans. Candida yeasts normally reside in the intestinal tract and can be found on mucous membranes and skin without causing infection; however, overgrowth of these organisms can cause symptoms to develop. Symptoms of candidiasis vary depending on the area of the body that is infected.
Candidiasis that develops in the mouth or throat is called “thrush” or oropharyngeal candidiasis. Candidiasis in the vagina is commonly referred to as a “yeast infection.” Invasive candidiasis occurs when Candida species enter the bloodstream and spread throughout the body. Click the links below for more information on the different types of Candida infections.
For other fungal topics, visit the fungal diseases homepage.
Global Emergence of Candida auris
Candida auris is an emerging fungus that presents a serious global health threat. Healthcare facilities in several countries have reported that C. auris has caused severe illness in hospitalized patients. C. auris is often resistant to multiple antifungal drugs.
- Page last reviewed: June 12, 2015
- Page last updated: August 7, 2017
- Content source:


 ShareCompartir
ShareCompartir