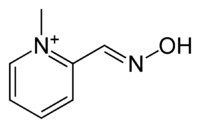
Pralidoxime
Pralidoxime (2-pyridine aldoxime methyl chloride) or 2-PAM, usually as the chloride or iodide salts, belongs to a family of compounds called oximes that bind to organophosphate-inactivated acetylcholinesterase.[1] It is used to treat organophosphate poisoning[2] in conjunction with atropine and diazepam. It is a white solid.
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | 1-methylpyridine-6-carbaldehyde oxime |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Micromedex Detailed Consumer Information |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.027.080 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C7H9N2O+ |
| Molar mass | 137.159 g/mol g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| (verify) | |
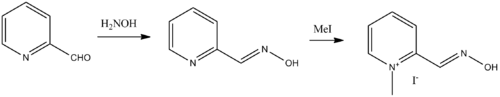
Chemical synthesis
Pralidoxime, 2-pyridinaldoxime methylchloride, is prepared by treating pyridine-2-carboxaldehyde with hydroxylamine. The resulting pyridine-2-aldoxime is alkylated with methyl iodide giving pralidoxime as the iodide salt.[3][4][5][6]
Mechanism of action
Pralidoxime is typically used in cases of organophosphate poisoning. Organophosphates such as sarin bind to the hydroxy component (the esteric site) of the active site of the acetylcholinesterase enzyme, thereby blocking its activity. Pralidoxime binds to the other half (the unblocked, anionic site) of the active site and then displaces the phosphate from the serine residue. The conjoined poison / antidote then unbinds from the site, and thus regenerates the fully functional enzyme.
Some phosphate-acetylcholinesterase conjugates continue to react after the phosphate docks to the esteric site, evolving into a more recalcitrant state. This process is known as aging. Aged phosphate-acetylcholinesterase conjugate are resistant to antidotes such as pralidoxime. Pralidoxime is often used with atropine (a muscarinic antagonist) to help reduce the parasympathetic effects of organophosphate poisoning. Pralidoxime is only effective in organophosphate toxicity. It has no beneficial effects if the acetylcholinesterase enzyme is carbamylated, as occurs with neostigmine, pyridostigmine, or insecticides such as carbaryl.
Pralidoxime has an important role in reversing paralysis of the respiratory muscles but due to its poor blood–brain barrier penetration, it has little effect on centrally-mediated respiratory depression. Atropine, which is choice of drug to antagonise the muscarinic effects of organophosphates, is administered even before pralidoxime during the treatment of organophosphate poisoning. While the efficacy of atropine has been well-established, clinical experience with pralidoxime has led to widespread doubt about its efficacy in treatment of organophosphorus poisoning.[7]
Dosage
- Adults: 30 mg/kg (typically 1-2 g), administered by intravenous therapy over 15–30 minutes, repeated 60 minutes later. It can also be given as a 500 mg/h continuous IV infusion.
- Children: 20–50 mg/kg followed by a maintenance infusion at 5–10 mg/kg/h.
Intravenous infusions can lead to respiratory or cardiac arrest if given too quickly.[8]
Interactions
When atropine and pralidoxime are used together, the signs of atropinization (flushing, mydriasis, tachycardia, dryness of the mouth and nose) may occur earlier than might be expected when atropine is used alone. This is especially true if the total dose of atropine has been large and the administration of pralidoxime has been delayed.
The following precautions should be kept in mind in the treatment of anticholinesterase poisoning, although they do not bear directly on the use of pralidoxime: since barbiturates are potentiated by the anticholinesterases, they should be used cautiously in the treatment of convulsions; morphine, theophylline, aminophylline, succinylcholine, reserpine, and phenothiazine-type tranquilizers should be avoided in patients with organophosphate poisoning.
Contraindications
There are no known absolute contraindications for the use of pralidoxime. Relative contraindications include known hypersensitivity to the drug and other situations in which the risk of its use clearly outweighs possible benefit.
See also
References
- Jokanović M.; Stojiljković, M. P. (2006). "Current understanding of the application of pyridinium oximes as cholinesterase reactivators in treatment of organophosphate poisoning". Eur J Pharmacol. 553: 10–7. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2006.09.054.
- Jokanović M, Prostran M (2009). "Pyridinium oximes as cholinesterase reactivators. Structure-activity relationship and efficacy in the treatment of poisoning with organophosphorus compounds". Curr. Med. Chem. 16 (17): 2177–88. doi:10.2174/092986709788612729. PMID 19519385.
- D. Nachmansonn, S. Ginsburg, U.S. Patent 2,816,113 (1957)
- L. P. Black, U.S. Patent 3,123,613 (1964)
- D.E. Easterday, A.A. Kondritzer, U.S. Patent 3,140,289 (1964)
- W.B. McDowell, U.S. Patent 3,155,674 (1964)
- [2]Banerjee I, Tripathi S K, Roy A S. Efficacy of pralidoxime in organophosphorus poisoning: Revisiting the controversy in Indian setting. J Postgrad Med 2014;60:27-30
- Baxter Healthcare Corporation 2006, Protopam Prescribing Information