Sciatic nerve
The sciatic nerve, also called the ischiadic or ischiadic nerve, is a large nerve in humans and other vertebrate animals which begins in the lower part of the sacral plexus and runs through the hip joint and down the lower limb. It is the longest and widest single nerve in the human body, going from the top of the leg to the foot on the posterior aspect.[1] The sciatic nerve provides the connection to the nervous system for nearly the whole of the skin of the leg, the muscles of the back of the thigh, and those of the leg and foot. It is derived from spinal nerves L4 to S3. It contains fibers from both the anterior and posterior divisions of the lumbosacral plexus.
| Sciatic nerve | |
|---|---|
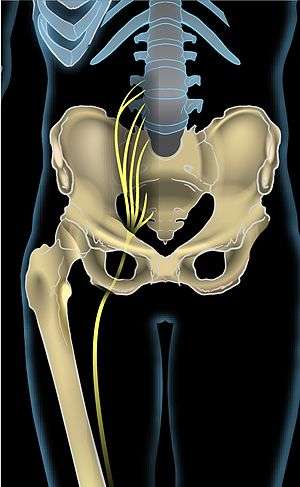 Right gluteal region, showing surface markings for arteries and sciatic nerve | |
| Details | |
| Pronunciation | /saɪˈætɪk/ |
| From | Lumbar and sacral plexus (L4-S3) |
| To | Tibial and common fibular nerve |
| Innervates | Lateral rotator group (except piriformis and quadratus femoris) and the posterior compartment of thigh |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | Nervus ischiadicus |
| MeSH | D012584 |
| TA | A14.2.07.046 |
| FMA | 19034 |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy | |
Structure
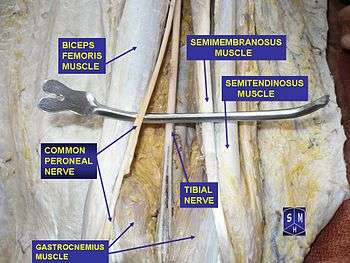
In humans, the sciatic nerve is formed from the L4 to S3 segments of the sacral plexus, a collection of nerve fibres that emerge from the sacral part of the spinal cord. The fibres unite to form a single nerve in front of the piriformis muscle. The nerve passes beneath piriformis and through the greater sciatic foramen, quitting the pelvis.[2]:422–4 From here, it travels down the posterior thigh to the popliteal fossa. The nerve travels in the posterior compartment of the thigh behind (superficial to) the adductor magnus muscle, and is itself in front of (deep to) the long head of the biceps femoris muscle. At the popliteal fossa, the nerve divides into its two branches:[2]:532
- The tibial nerve, which travels down the posterior compartment of the leg into the foot
- The common peroneal nerve (also called the common fibular nerve), which travels down the anterior and lateral compartments of the leg into the foot
The sciatic nerve is the largest nerve in the human body.[2]:422–4
Development
Function
The sciatic nerve supplies sensation to the skin of the foot, as well as the entire lower leg (except for its inner side). Sensation to skin to the sole of the foot is provided by the tibial nerve, and the lower leg and upper surface of the foot via the common peroneal nerve.[2]:422–4
The sciatic nerve also innervates muscles. In particular:[2]:422–4
- Via the tibial nerve, the muscles in the posterior compartment of the leg and sole of the foot (plantar aspect).[lower-alpha 1]
- Via the common peroneal nerve, the muscles in the anterior and lateral compartments of the leg.[lower-alpha 2]
Clinical significance
Sciatica
Pain caused by a compression or irritation of the sciatic nerve by a problem in the lower back is called sciatica. Common causes of sciatica include the following lower back and hip conditions: spinal disc herniation, degenerative disc disease, lumbar spinal stenosis, spondylolisthesis, and piriformis syndrome.[3] Other acute causes of sciatica include coughing, muscular hypertension, and sneezing.[4]
Injury
Sciatic nerve injury occurs between 0.5% and 2.0% of the time during a hip replacement.[5] Sciatic nerve palsy is a complication of total hip arthroplasty with an incidence of 0.2% to 2.8% of the time, or with an incidence of 1.7% to 7.6% following revision.[6] Following the procedure, in rare cases, a screw, broken piece of trochanteric wire, fragment of methyl methacrylate bone cement, or of a Burch-Schneider antiprofusio cage can impinge on the nerve; this can cause sciatic nerve palsy which may resolve after the fragment is removed and the nerve freed. The nerve can be surrounded in oxidized regenerated cellulose to prevent further scarring. Sciatic nerve palsy can also result from severe spinal stenosis following the procedure, which can be addressed by spinal decompression surgery.[5][7] It is unclear if inversion therapy is able to decompress the sacral vertebrae, it may only work on the lumbar aspects of the sciatic nerves.
Sciatic nerve injury may also occur from improperly performed injections into the buttock, and may result in sensory loss.[8]:66
Other disease
Bernese periacetabular osteotomy resulted in major nerve deficits in the sciatic or femoral nerves in 2.1% of 1760 patients, of whom approximately half experienced complete recovery within a mean of 5.5 months.[9]
Sciatic nerve exploration can be done by endoscopy in a minimally invasive procedure to assess lesions of the nerve.[10] Endoscopic treatment for sciatic nerve entrapment has been investigated in deep gluteal syndrome. Patients were treated with sciatic nerve decompression by resection of fibrovascular scar bands, piriformis tendon release, obturator internus, or quadratus femoris or by hamstring tendon scarring.[11]
Anesthetic
Signals from the sciatic nerve and its branches can be blocked, in order to interrupt transmission of pain signal from the innervation area, by performing a regional nerve blockade called a sciatic nerve block.
Society and culture
According to Jewish law, the sciatic nerve (Hebrew: Gid hanasheh) cannot be eaten, to commemorate Jacob's hurt in his struggle with an Angel.[12]
Additional images
 Sciatic nerve.
Sciatic nerve.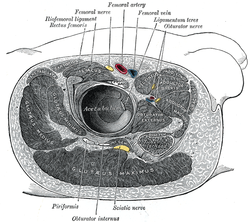 Structures surrounding left hip-joint.
Structures surrounding left hip-joint.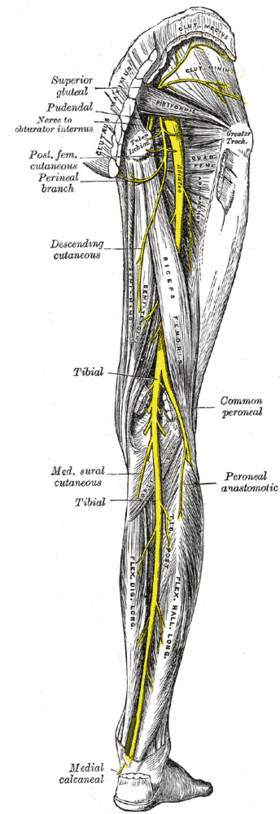 Nerves of the right lower extremity. Posterior view.
Nerves of the right lower extremity. Posterior view.- Sciatic nerve.
- Sciatic nerve.
- Sciatic nerve.
See also
Notes
- Namely the flexor hallicus longus, flexor digitorum longus, tibialis posterior and popliteus of the deep part of the compartment, and the gastrocnemius, soleus and plantaris of the superficial part of the compartment.
- Namely the tibialis anterior, extensor hallucis longus, extensor digitorum longus, and fibularis tertius (peroneus tertius) of the anterior compartment, and the Fibularis longus and brevis of the lateral compartment.
References
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 960 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
- "sciatic nerve (anatomy)". Britannica Online Encyclopedia. Retrieved 23 April 2012.
- Drake, Richard L.; Vogl, Wayne; Tibbitts, Adam W.M. Mitchell; illustrations by Richard; Richardson, Paul (2005). Gray's anatomy for students. Philadelphia: Elsevier/Churchill Livingstone. ISBN 978-0-8089-2306-0.
- "Sciatica - Topic Overview". WebMD. 21 July 2010. Retrieved 23 April 2012.
- "What is sciatica: What causes sciatica?". MedicalBug. 11 April 2012. Retrieved 23 April 2012.
- Stiehl JB, Stewart WA (1998). "Late sciatic nerve entrapment following pelvic plate reconstruction in total hip arthroplasty". J Arthroplasty. 13 (5): 586–8. doi:10.1016/s0883-5403(98)90060-2. PMID 9726326.
- Alessandro Bistolfi; et al. (2011). "Operative Management of Sciatic Nerve Palsy due to Impingement on the Metal Cage after Total Hip Revision: Case Report". Case Rep Med. 2011: 1–3. doi:10.1155/2011/830296. PMC 3163138. PMID 21876701.
- Abitbol JJ, Gendron D, Laurin CA, Beaulieu MA (1990). "Gluteal nerve damage following total hip arthroplasty. A prospective analysis". J Arthroplasty. 5 (4): 319–22. doi:10.1016/s0883-5403(08)80090-3. PMID 2290087.is cited by Stiehl and Stewart for the 0.5-2.0% figure.
- James, William D.; Berger, Timothy G.; et al. (2006). Andrews' Diseases of the Skin: clinical Dermatology. Saunders Elsevier. ISBN 978-0-7216-2921-6.
- Sierra RJ, Beaule P, Zaltz I, Millis MB, Clohisy JC, Trousdale RT (2012). "Prevention of nerve injury after periacetabular osteotomy". Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 470 (8): 2209–19. doi:10.1007/s11999-012-2409-1. PMC 3392380. PMID 22684336.
- Mobbs RJ, Teo C (2004). "Endoscopic-assisted sciatic nerve exploration". Minim Invasive Neurosurg. 47 (3): 178–80. doi:10.1055/s-2004-818488. PMID 15343436.
- Martin HD, Shears SA, Johnson JC, Smathers AM, Palmer IJ (2011). "The endoscopic treatment of sciatic nerve entrapment/deep gluteal syndrome". Arthroscopy. 27 (2): 172–81. doi:10.1016/j.arthro.2010.07.008. PMID 21071168.
- Goldberger, Moshe. "1: Not to Eat the Gid HaNasheh". The First Prohibitions. Retrieved 10 March 2014.
External links
- Sciatic_nerve at the Duke University Health System's Orthopedics program
- MedlinePlus Image 19503
- pelvis at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University) (pelvicnerves)
- glutealregion at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University) (glutealner)
- Sciatica and the Sciatic Nerve