Doing Business with Us

As we work towards our ambitious but achievable goal of ending the HIV/AIDS epidemic by 2030, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) continues our vital work with partners from around the world. CDC maintains strong, collaborative partnerships with country governments including Ministries of Health, as well as non-governmental organizations, leading universities, faith-based organizations, multilateral organizations, and the private sector.
CDC funds partners through Funding Opportunity Announcements posted each year on Grants.gov. The projects focused on fighting global HIV/AIDS are part of the US President’s Emergency Plan for AIDS Relief’s work with partners to control the HIV/AIDS epidemic in each country to achieve a sustainable response.
Frequently Asked Questions
How and where does the US Government fund HIV/AIDS work internationally?
The US Government funds HIV/AIDS programs internationally through the US President’s Emergency Plan for AIDS Relief (PEPFAR). PEPFAR works in countries worldwide affected by HIV/AIDS.
What is PEPFAR?
PEPFAR is the U.S. Government initiative to help save the lives of those suffering from HIV/AIDS around the world. This historic commitment is the largest by any nation to combat a single disease internationally, and PEPFAR investments also help alleviate suffering from other diseases across the global health spectrum. For more information, visit www.pepfar.gov.
What is CDC’s role in PEPFAR?
As America’s leading science-based public health and disease prevention agency, CDC plays a central role in PEPFAR. CDC uses our technical expertise in public health science and long-standing relationships with Ministries of Health across the globe to work side-by-side with countries to build strong national programs and sustainable public health systems. These partners support countries to respond effectively to the global HIV/AIDS epidemic and to other diseases that threaten the health and prosperity of the global community at large. For more information, visit www.cdc.gov/globalaids/
Does CDC provide direct care in countries?
No. CDC has long-standing relationships with Ministries of Health. We work side-by-side with Ministries of Health in 44 countries to build their capacity to lead and manage their national HIV/AIDS programs by providing direct technical assistance and knowledge transfer. We work with countries to build high-quality laboratory systems and services that are critical for HIV prevention, care and treatment, as well as for other diseases.
How does CDC determine which programs it will fund each year?
The US Government funds HIV/AIDS programs internationally through PEPFAR. As one of the PEPFAR implementing agencies, CDC funding for global HIV/AIDS is programmed through the PEPFAR Country Operational Plans and Regional Operational Plans. These plans cover all PEPFAR-funded agencies that are currently operating in foreign countries. For more information, visit www.pepfar.gov/countries/cop/index.htm.
PEPFAR country budgets and activities are submitted through the PEPFAR Country Operational Plans and Regional Operational Plans by the PEPFAR country teams. These plans are then approved by the U.S. Global AIDS Coordinator, and funded by the US Congress. More information on PEPFAR finding can be found at https://data.pepfar.net/
How does CDC decide which projects to fund in countries?
The funding process is a several step process:
Through a thorough analysis of their current portfolio of projects and a consideration of PEPFAR priorities, CDC field offices in country determine if any shifts in programmatic focus or funding are needed, and if there are unmet needs.
Current awards that are due to expire also are reviewed to determine if they include activities that should be continued through an additional, follow-on award.
Once the portfolio review is complete and specific projects are agreed and approved, CDC field offices draft a Funding Opportunity Announcement. These undergo a rigorous review by technical and funding subject matter experts.
Once a draft Funding Opportunity Announcement has completed a full review, it is published on grants.gov. This allows interested organizations to apply for funding. Partners have 60 days to respond from the date a Funding Opportunity Announcement is posted.
Once all applications are received, each application is reviewed and scored against the criteria listed in the Funding Opportunity Announcement. This review process is known as objective reviews, or “Objective Review Panels”.
The CDC field offices make awards based on the Objective Review Panel results, and applicants are notified.
How does CDC determine the funding levels for each award?
The overall funding for each project is determined in the PEPFAR Country Operational Plans and Regional Operational Plans through the process described above.
Each award is planned with a funding ceiling, which is the maximum potential funding level. The final funding level is subject to the awardee’s ability to receive and expend funds, as well as the availability of PEPFAR funds.
The overall funding level may change from year to year depending upon the approved work plan and funds made available to CDC by the US Congress.
How does CDC select partners to fund?
All grants awarded through CDC follow standard US Government processes. Information on the US Government’s grant management process can be found at www.grants.gov/web/grants/learn-grants.html.
Funding opportunities are posted at www.grants.gov.
Are all CDC projects competitively awarded?
CDC follows US Government regulations regarding grant making. As such, CDC projects are competitively awarded except in select cases where a direct award is deemed appropriate in line with US Government regulations. For more information on the awards criteria and USG regulations regarding grant making, visit www.grants.gov/web/grants/learn-grants/grant-policies.html.
Does CDC make the results of Objective Review Panels publicly available?
Organizations who have successfully applied for recent awards and received funding can be found here
Where can I find the Funding Opportunity Announcements that are currently open for applications?
All current funding opportunities are listed at www.grants.gov/
Does CDC fund local partners?
Yes. Reflecting PEPFAR’s commitment to country ownership, CDC is a strong supporter of local indigenous organizations. Overall, CDC invests more resources into local, indigenous partners than international partners.
CDC has many international partners. I am concerned that this funding doesn’t reach the beneficiary countries. Is this true?
No. For international partners, funding is still spent directly in the partner country, benefiting people living with and affected by HIV/AIDS and helping to also prevent transmission of the disease in that country. Funds awarded to international organizations also include sub grants to local organizations that also directly support partner countries.
Current Partnerships
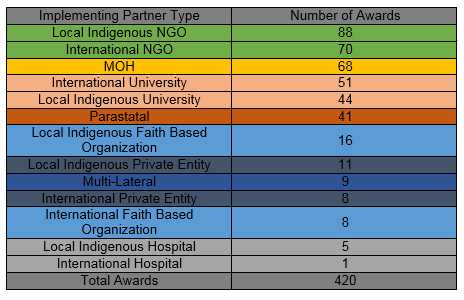
In fiscal year 2015, CDC through the US President’s Emergency Plan for AIDS Relief had a total of 420 cooperative agreements with organizations around the world in support of the ambitious but achievable goal of ending the HIV/AIDS epidemic by 2030.
Reflecting PEPFAR’s commitment to country ownership, CDC is a strong supporter of local indigenous organizations. Overall, CDC invests more resources into local, indigenous partners than international.
For international partners, funding is still spent directly in the partner country, benefitting people living with and affected by HIV/AIDS. Funds awarded to international organizations also include sub grants to local organizations that also directly support partner countries.
CDC Active Cooperative Agreements for global HIV/AIDS, by Organization Type, as of November 1, 2015
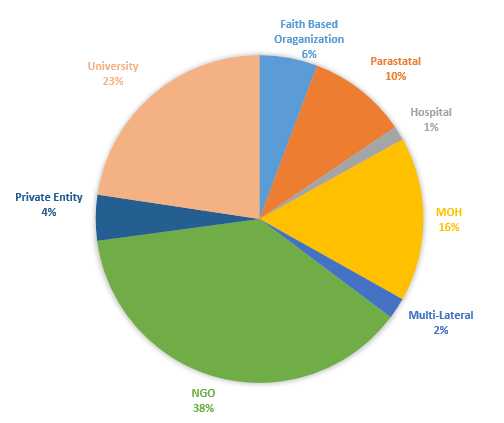
CDC Active Cooperative Agreements for global HIV/AIDS, by Implementing Partner Type, as of November 1, 2015
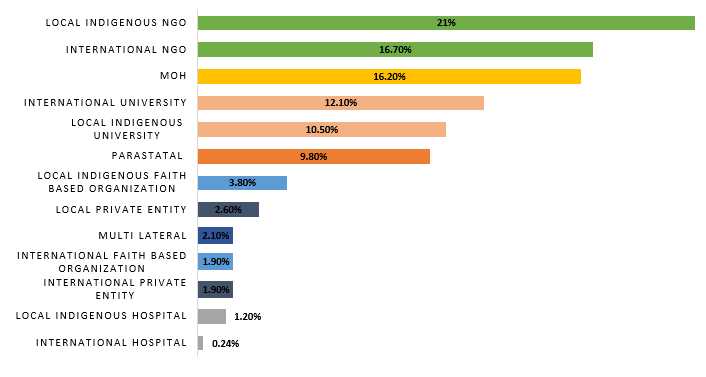
CDC Active Cooperative Agreements for global HIV/AIDS, by Implementing Partner Type, as of November 1, 2015
Definitions of Implementing Partner Types
- Non-Governmental Organization: A legally constituted organization created by natural or legal persons that operates independently from any government
- Ministry of Health: Government entity focused on issues related to the general health of the citizens
- Parastatal: A foreign government entity that is not a Ministry of Health
- Multi-Lateral: An organization formed between three or more nations to work on issues that relate to all of the countries in the organization
- Private Entity: Any entity other than a State, local government, Indian tribe, or foreign public entity
Funding Trends Over Time
CDC Funding Trends for Global HIV/AIDS over Time
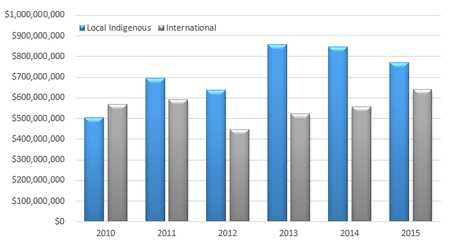
When funding international partners. Money is still spent in the country of operation. The awarded funds include sub grants to local organizations and the majority is expended in country.
The overall trend is that CDC invests more resources into local/indigenous partners than international.
Recent Cooperative Agreements
Funding Opportunity Announcement Questions and Answers
Please note all CDC's Division of Global HIV/AIDS (DGHA) Funding Opportunity Announcements (FOAs) are officially posted and advertised on grants.gov.This website is used to post Question/Answers and additional information regarding DGHA FOAs. All formal amendments, changes, and updates to FOAs can be found at grants.gov. It is not possible to submit applications, questions, or seek help with application submission via this site. For all application submissions and inquiries, please go to grants.gov.
Current DGHA FOAs
- 12 18 2015 Caribbean CDC-RFA-GH16-1607
- 12 18 2015 Ethiopia CDC-RFA-GH16-1614
- 12 18 2015 Malawi CDC-RFA-GH16-1630
- 12 18 2015 Namibia CDC-RFA-GH16-1640
- 12 18 2015 Zimbabwe CDC-RFA-GH16-1673
- 12 19 2015 Haiti CDC-RFA-GH16-1680
- 12 19 2015 Kenya CDC-RFA-GH16-1619
- 12 19 2015 Kenya CDC-RFA-GH16-1620
- 12 19 2015 Kenya CDC-RFA-GH16-1621
- 12 19 2015 Kenya CDC-RFA-GH16-1624
- 12 19 2015 Kenya CDC-RFA-GH16-1628
- 12 19 2015 Kenya CDC-RFA-GH16-1690
- 12 19 2015 Kenya CDC-RFA-GH16-1700
- 12 19 2015 Kenya CDC-RFA-GH16-1701
- 12 19 2015 Kenya CDC-RFA-GH16-1716
- 12 19 2015 Kenya CDC-RFA-GH16-1717
- 12 19 2015 Malawi CDC-RFA-GH16-1629
- 12 19 2015 Nigeria CDC-RFA-GH16-1642
- 12 19 2015 Swaziland CDC-RFA-GH16-1646
- 12 19 2015 Tanzania CDC-RFA-GH16-1650
- 12 19 2015 Zimbabwe CDC-RFA-GH16-1674
- 12 22 2015 Tanzania CDC-RFA-GH16-1648
- 12 19 2015 Zimbabwe CDC-RFA-GH16-1675
- 12 23 2015 Haiti CDC-RFA-GH16-1682
- 12 23 2015 Haiti CDC-RFA-GH16-1710
- 12 23 2015 Haiti CDC-RFA-GH16-1711
- 12 23 2015 Tanzania CDC-RFA-GH16-1652
- 12 24 2015 Cote d'Ivoire CDC-RFA-GH16-1612
- 12 24 2015 Democratic Republic of Congo CDC-RFA-GH16-1613
- 12 24 2015 Haiti CDC-RFA-GH16-1712
- 12 24 2015 Tanzania CDC-RFA-GH16-1647
- 12 23 2015 Tanzania CDC-RFA-GH16-1653
- 12 23 2015 Zambia CDC-RFA-GH16-1668.pdf
- 12 23 2015 Zambia CDC-RFA-GH16-1669.pdf
- 12 23 2015 Zambia CDC-RFA-GH16-1670.pdf
- 12 24 2015 Namibia CDC-RFA-GH16-1639.pdf
- 12 30 2015 Headquarters CDC-RFA-GH16-1688.pdf
- 12 30 2015 Mozambique CDC-RFA-GH16-1632.pdf
- 12 30 2015 Mozambique CDC-RFA-GH16-1634.pdf
- 12 30 2015 Headquarters CDC-RFA-GH16-1689.pdf
- 12 30 2015 South Africa CDC-RFA-GH16-1645.pdf
To view all of the Funding Opportunity Announcement Q&A's
- Page last reviewed: August 21, 2016
- Page last updated: August 21, 2016
- Content source:


 ShareCompartir
ShareCompartir