Rolapitant
Rolapitant (INN,[2] trade name Varubi /vəˈruːbi/ və-ROO-bee in the US and Varuby in Europe) is a drug originally developed by Schering-Plough and licensed for clinical development by Tesaro, which acts as a selective NK1 receptor antagonist (antagonist for the NK1 receptor).[3] It has been approved as a medication for the treatment of chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting (CINV) after clinical trials showed it to have similar or improved efficacy and some improvement in safety over existing drugs for this application.[4][5][6][7]
.svg.png) | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Pronunciation | /roʊˈlæpɪtænt/ roh-LAP-i-tant |
| Trade names | Varubi (US), Varuby (EU) |
| Other names | SCH 619734 |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | varubi |
| License data | |
| Routes of administration | By mouth (tablets) |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | nearly 100% |
| Protein binding | 99.8% |
| Metabolism | CYP3A4 |
| Metabolites | C4-pyrrolidine-hydroxylated rolapitant (major) |
| Elimination half-life | 169–183 hours |
| Excretion | Feces (52–89%), urine (9–20%)[1] |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.243.022 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C25H26F6N2O2 |
| Molar mass | 500.476 g/mol g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
Medical uses
Rolapitant is used in combination with other antiemetic (anti-vomiting) agents in adults for the prevention of delayed nausea and vomiting associated with initial and repeat courses of emetogenic cancer chemotherapy, including, but not limited to, highly emetogenic chemotherapy.[1] The approved antiemetic combination consists of rolapitant plus dexamethasone and a 5-HT3 antagonist.[8]
Contraindications
Under the US approval, rolapitant is contraindicated in combination with thioridazine, whose inactivation could be inhibited by rolapitant.[9] Under the European approval, it is contraindicated in combination with St. John's Wort, which is expected to accelerate inactivation of rolapitant.[8]
Side effects
In studies comparing chemotherapy plus rolapitant, dexamethasone and a 5-HT3 antagonist to chemotherapy plus placebo, dexamethasone and a 5-HT3 antagonist, most side effects had comparable frequencies in both groups, and differed more between chemotherapy regimens than between rolapitant and placebo groups. Common side effects included decreased appetite (9% under rolapitant vs. 7% under placebo), neutropenia (9% vs. 8% or 7% vs. 6%, depending on the kind of chemotherapy), dizziness (6% vs. 4%), indigestion and stomatitis (both 4% vs. 2%).[9]
Overdose
Up to eightfold therapeutic doses have been given in studies without problems.[8]
Interactions
Rolapitant moderately inhibits the liver enzyme CYP2D6. Blood plasma concentrations of the CYP2D6 substrate dextromethorphan have increased threefold when combined with rolapitant; and increased concentrations of other substrates are expected. The drug also inhibits the transporter proteins ABCG2 (breast cancer resistance protein, BCRP) and P-glycoprotein (P-gp), which has been shown to increase plasma concentrations of the ABCG2 substrate sulfasalazine twofold and the P-gp substrate digoxin by 70%.[8]
Strong inducers of the liver enzyme CYP3A4 decrease the area under the curve of rolapitant and its active metabolite (called M19); for rifampicin, this effect was almost 90% in a study. Inhibitors of CYP3A4 have no relevant effect on rolapitant concentrations.[8]
Pharmacology
Pharmacodynamics
Both rolapitant and its active metabolite M19 block the NK1 receptor with high affinity and selectivity: to block the closely related receptor NK2 or any other of 115 tested receptors and enzymes, more than 1000-fold therapeutic concentrations are necessary.[10]
Pharmacokinetics
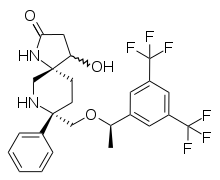
Rolapitant is practically completely absorbed from the gut, independently of food intake. It undergoes no measurable first-pass effect in the liver. Highest blood plasma concentrations are reached after about four hours. When in the bloodstream, 99.8% of the substance are bound to plasma proteins.[8]
It is metabolized by the liver enzyme CYP3A4, resulting in the major active metabolite M19 (C4-pyrrolidine-hydroxylated rolapitant) and a number of inactive metabolites. Rolapitant is mainly excreted via the feces (52–89%) in unchanged form, and to a lesser extent via the urine (9–20%) in form of its inactive metabolites. Elimination half-life is about seven days (169 to 183 hours) over a wide dosing range.[8]
Chemistry
The drug is used in form of rolapitant hydrochloride monohydrate, a white to off-white, slightly hygroscopic crystalline powder. Its maximum solubility in aqueous solutions is at pH 2–4.[10]
See also
References
- "Varubi (rolapitant) Tablets, for Oral Use. Full Prescribing Information" (PDF). TESARO, Inc. 1000 Winter St., #3300, Waltham, MA 02451.
- "International Nonproprietary Names for Pharmaceutical Substances (INN). Recommended International Nonproprietary Names (Rec. INN): List 59" (PDF). World Health Organization. p. 64. Retrieved 5 October 2016.
- Duffy, R. A; Morgan, C; Naylor, R; Higgins, G. A; Varty, G. B; Lachowicz, J. E; Parker, E. M (2012). "Rolapitant (SCH 619734): a potent, selective and orally active neurokinin NK1 receptor antagonist with centrally-mediated antiemetic effects in ferrets". Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 102 (1): 95–100. doi:10.1016/j.pbb.2012.03.021. PMID 22497992.
- Jordan, K; Jahn, F; Aapro, M (2015). "Recent developments in the prevention of chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting (CINV): a comprehensive review". Ann Oncol. 26 (6): 1081–90. doi:10.1093/annonc/mdv138. PMID 25755107.
- Nasir, S. S; Schwartzberg, L. S (2016). "Recent Advances in Preventing Chemotherapy-Induced Nausea and Vomiting". Oncology. 30 (8): 750–62. PMID 27539626.
- Rapoport, B; Schwartzberg, L; Chasen, M; Powers, D; Arora, S; Navari, R; Schnadig, I (2016). "Efficacy and safety of rolapitant for prevention of chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting over multiple cycles of moderately or highly emetogenic chemotherapy". Eur J Cancer. 57: 23–30. doi:10.1016/j.ejca.2015.12.023. PMID 26851398.
- Chasen, M. R; Rapoport, B. L (2016). "Rolapitant for the treatment of chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting: a review of the clinical evidence". Future Oncol. 12 (6): 763–78. doi:10.2217/fon.16.11. PMID 26842387.
- "Varuby: EPAR – Product Information" (PDF). European Medicines Agency. 2017-05-31.
- FDA Professional Drug Information on Varubi. Accessed 2017-10-11.
- "Varuby: EPAR – Public assessment report" (PDF). European Medicines Agency. 2017-05-31.