Ilepcimide
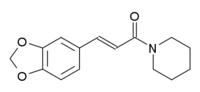
Ilepcimide, also known as antiepilepserine, is a anticonvulsant.[1] It is a piperidine derivative that was first synthesized by Chinese researchers as an analogue of piperine, the main alkaloid and phytochemical of black pepper (and of other plants in the family Piperaceae).
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C15H17NO3 |
| Molar mass | 259.300 g/mol g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| | |
Ilepcimide has serotonergic activity.[1][2][3]
See also
- Black pepper
References
- C.R. Ganellin; David J. Triggle (21 November 1996). Dictionary of Pharmacological Agents. CRC Press. p. 1116. ISBN 978-0-412-46630-4. Retrieved 30 November 2012.
- Liu, G.Q., Algeria, S., Ceci, A., Gerattini, S., Gobi, M. and Murai, S. (1984). "Stimulation of serotonin synthesis in rat brain after antiepilepserine, an antiepileptic piperine derivative". Biochemical Pharmacology. 33: 3883–3886. doi:10.1016/0006-2952(84)90055-8.CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
- Yan, Q.S., Mishra, P.K., Burger, R.L., Bettendorf, A.F., Jobe, P.C. and Dailey J.W. (1992). "Evidence that carbamazepine and antiepilepserine may produce a component of their anticonvulsant effects by activating serotonergic neurons in genetically epilepsy-prone rats". J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 261 (2): 652–659.CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative
Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.