Superior orbital fissure
The superior orbital fissure is a foramen in the skull, although strictly it is more of a cleft, lying between the lesser and greater wings of the sphenoid bone.
| Superior orbital fissure | |
|---|---|
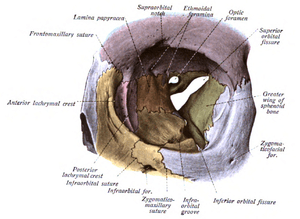 Orbit seen from the front, with bones labeled in different colors, and superior orbital fissure at center as an "hour-glass" formation. | |
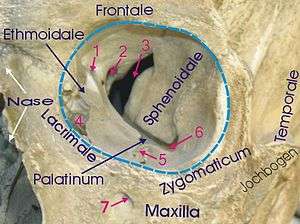 1 Foramen ethmoidale, 2 Canalis opticus, 3 Fissura orbitalis superior, 4 Fossa sacci lacrimalis, 5 Sulcus infraorbitalis, 6 Fissura orbitalis inferior, 7 Foramen infraorbitale | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | fissura orbitalis superior |
| TA | A02.1.05.023 A02.1.00.083 |
| FMA | 54799 |
| Anatomical terms of bone | |
Structures passing through
A number of important anatomical structures pass through the fissure, and these can be damaged in orbital trauma, particularly blowout fractures through the floor of the orbit into the maxillary sinus. These structures are:
- superior and inferior divisions of oculomotor nerve (III)
- trochlear nerve (IV)
- lacrimal, frontal and nasociliary branches of ophthalmic (V1).
- abducens nerve (VI)
- superior and inferior divisions of ophthalmic vein. Inferior division also passes through the inferior orbital fissure.
- sympathetic fibers from cavernous plexus
These include nonvisual sensory messages, such as pain, or motor nerves. They also serve as vascular connections.[1]
The nerves passing through the fissure can be remembered with the mnemonic, "Live Frankly To See Absolutely No Insult" - for Lacrimal and Frontal divisions of the ophthalmic nerve (V1), Trochlear nerve (IV), Superior division of the oculomotor nerve (III), Abducens nerve (VI), Nasociliary branch of the ophthalmic nerve (V1) and Inferior Division of the oculomotor nerve (III).[2]
It is divided into 3 parts from lateral to medial:
- Lateral part transmits: superior ophthalmic vein, lacrimal nerve, frontal nerve, trochlear nerve (CN IV), recurrent meningeal branch of lacrimal artery (anastomotic branch of lacrimal artery with the middle meningeal artery)
- Middle part transmits: Superior and inferior divisions of the oculomotor nerve (CN III), nasociliary nerve (lies between the two divisions of oculomotor nerve) and abducent nerve
- Medial part transmits: Inferior ophthalmic veins and sympathetic nerves arising from the plexus that accompanies the internal carotid artery
Pathology
The abducens nerve is most likely to show signs of damage first, with the most common complaints retro-orbital pain and the involvement of cranial nerves III, IV, V1, and VI without other neurological signs or symptoms. This presentation indicates either compression of structures in the superior orbital fissure or the cavernous sinus.
Superior orbital fissure syndrome
Superior orbital fissure syndrome, also known as Rochon-Duvigneaud's syndrome,[3][4] is a neurological disorder that results if the superior orbital fissure is fractured. Involvement of the cranial nerves that pass through the superior orbital fissure may lead to diplopia, paralysis of extraocular muscles, exophthalmos, and ptosis. Blindness or loss of vision indicates involvement of the orbital apex, which is more serious, requiring urgent surgical intervention. Typically, if blindness is present with superior orbital syndrome, it is called orbital apex syndrome.
References
- "eye, human."Encyclopædia Britannica from Encyclopædia Britannica 2006 Ultimate Reference Suite DVD
- "Superior orbital fissure: Structures passing through". http://www.lifehugger.com/. LifeHugger. Retrieved 2009-12-11. External link in
|website=(help) - synd/3387 at Who Named It?
- A. Rochon-Duvigneaud. Quelques cas de paralysie de tous les nerfs orbitaires (ophthalmoplegie totale avec amaurosse en anesthésie dans le domaine de l’ophthalmique d’origine syphilitique). Archives d'ophthalmologie, Paris, 1896, 16: 746-760.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Superior orbital fissure. |
- Anatomy figure: 22:02-04 at Human Anatomy Online, SUNY Downstate Medical Center
- lesson3 at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University) (orbitforamina) (#2)