Foramen spinosum
The foramen spinosum is one of two foramina located in the base of the human skull, on the sphenoid bone. It is situated just anterior to the spine of the sphenoid bone, and just lateral to the foramen ovale. The middle meningeal artery, middle meningeal vein, and the meningeal branch of the mandibular nerve pass through the foramen.
| Foramen spinosum | |
|---|---|
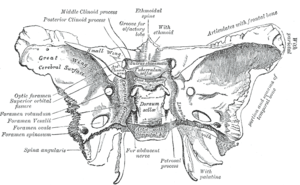 The inner surface of the sphenoid bone, with the foramen spinosum labelled at the left, second from the bottom. | |
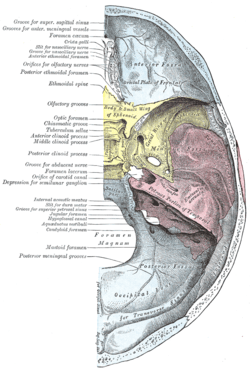 The inner surface of the base of the skull, with the sphenoid bone yellowed. The foramen spinosum is visible at the bottom right of the bone. | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | Foramen spinosum |
| TA | A02.1.05.038 |
| FMA | 53156 |
| Anatomical terms of bone | |
The foramen spinosum is often used as a landmark in neurosurgery, due to its close relations with other cranial foramina. It was first described by Jakob Benignus Winslow in the 18th century.
Structure
The foramen spinosum is a foramen through the sphenoid bone situated in the middle cranial fossa.[1][2]:771 It is one of two foramina in the greater wing of the sphenoid bone. The foramen ovale is one of these two cranial foramina, situated directly anterior and medial to the foramen spinosum.[2]:776 The spine of sphenoid falls medial and posterior to the foramen. Lateral to the foramen is the mandibular fossa,[2]:873 and posterior is the Eustachian tube.[1]
Variation
The foramen spinosum varies in size and location. The foramen is rarely absent, usually unilaterally, in which case the middle meningeal artery enters the cranial cavity through the foramen ovale.[3] It may be incomplete, which may occur in almost half of the population. Conversely, in a minority of cases (less than 1%), it may also be duplicated, particularly when the middle meningeal artery is also duplicated.[1][3]
The foramen may pass through the sphenoid bone at the apex of the spinous process, or along its medial surface.[1]
Development
In the newborn, the foramen spinosum is about 2.25 mm long and in adults about 2.56 mm. The width of the foramen extends from 1.05 mm to about 2.1 mm in adults.[4] The average diameter of the foramen spinosum is 2.63 mm in adults.[5]
The earliest perfect ring-shaped formation of the foramen spinosum was observed in the eighth month after birth and the latest seven years after birth in a developmental study of the foramen rotundum, foramen ovale and foramen spinosum. The majority of the foramina in the skull studies were round in shape.[5] The sphenomandibular ligament, derived from the first pharyngeal arch and usually attached to the spine of the sphenoid bone, may be found attached to the rim of the foramen.[1][6]
Animals
In other great apes, the foramen spinosum is found not in the sphenoid bone but in parts of the temporal bone such as the squamous part, found at the sphenosquamosal suture, or absent.[1][7]
Function
The foramen spinosum permits the passage of the middle meningeal artery, middle meningeal vein, and the meningeal branch of the mandibular nerve.[1][2]:763
Clinical significance
Due to its distinctive position, the foramen is used as an anatomical landmark during neurosurgery. As a landmark, the foramen spinosum reveals the positions of other cranial foramina, the mandibular nerve and trigeminal ganglion, foramen ovale, and foramen rotundum. It may also be relevant in achieving haemostasis during trauma surgery.[1]
History
The foramen spinosum was first described by the Danish anatomist Jakob Benignus Winslow in the 18th century. It is so-named because of its relationship to the spinous process of the greater wing of the sphenoid bone. However, due to incorrectly declining the noun, the literal meaning is "hole full of thorns" (Latin: foramen spinosum). The correct, but unused name would, in fact, be foramen spinae.[1]
Additional images
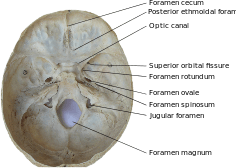 Inner surface of the base of skull, showing cranial foramina
Inner surface of the base of skull, showing cranial foramina
References
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 150 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
- Krayenbühl, Niklaus; Isolan, Gustavo Rassier; Al-Mefty, Ossama (2 August 2008). "The foramen spinosum: a landmark in middle fossa surgery" (PDF). Neurosurgical Review. 31 (4): 397–402. doi:10.1007/s10143-008-0152-6.
- Drake, Richard L.; Vogl, Wayne; Tibbitts, Adam W.M. Mitchell; illustrations by Richard; Richardson, Paul (2005). Gray's anatomy for students. Philadelphia: Elsevier/Churchill Livingstone. ISBN 978-0-8089-2306-0.
- "Illustrated Encyclopedia of Human Anatomic Variation: Opus V: Skeletal Systems: Cranium – Sphenoid Bone". Illustrated Encyclopedia of Human Anatomic Variation. Retrieved 2006-04-10.
- Lang J, Maier R, Schafhauser O (1984). "Postnatal enlargement of the foramina rotundum, ovale et spinosum and their topographical changes". Anatomischer Anzeiger. 156 (5): 351–87. PMID 6486466.
- Yanagi S (1987). "Developmental studies on the foramen rotundum, foramen ovale and foramen spinosum of the human sphenoid bone". The Hokkaido Journal of Medical Science. 62 (3): 485–96. PMID 3610040.
- Ort, Bruce Ian Bogart, Victoria (2007). Elsevier's integrated anatomy and embryology. Philadelphia, Pa.: Elsevier Saunders. p. Elsevier’s Integrated Anatomy and Embryology. ISBN 978-1-4160-3165-9.
- Braga, J.; Crubézy, E.; Elyaqtine, M. (1998). "The posterior border of the sphenoid greater wing and its phylogenetic usefulness in human evolution". American Journal of Physical Anthropology. 107 (4): 387–399. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1096-8644(199812)107:4<387::AID-AJPA2>3.0.CO;2-Y. PMID 9859876.
External links
- Anatomy photo:22:os-0902 at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center – "Osteology of the Skull: Internal Surface of Skull"
- Anatomy figure: 27:02-03 at Human Anatomy Online, SUNY Downstate Medical Center – "Schematic view of key landmarks of the infratemporal fossa."
- Anatomy of the Skull – 27. Foramen spinosum