Orbital lamina of ethmoid bone
The orbital lamina of ethmoid bone, (or lamina papyracea or orbital lamina) is a smooth, oblong bone plate which forms the lateral surface of the labyrinth of the ethmoid bone in the skull. The plate covers in the middle and posterior ethmoidal cells and forms a large part of the medial wall of the orbit.
| Orbital lamina of ethmoid bone | |
|---|---|
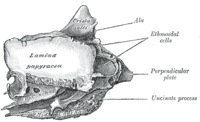 Ethmoid bone from the right side. (Lamina papyracea visible at center left.) | |
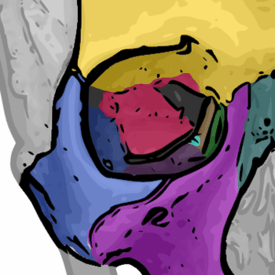 The seven bones which articulate to form the orbit. (Ethmoid is brown.) | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | Lamina orbitalis ossis ethmoidalis |
| Anatomical terminology | |
It articulates above with the orbital plate of the frontal bone, below with the maxilla and the orbital process of palatine bone, in front with the lacrimal, and behind with the sphenoid.
Its name lamina papyracea is an appropriate description, as this part of the ethmoid bone is paper-thin and fractures easily. A fracture here could cause entrapment of the medial rectus muscle.
Additional Images
- Orbital lamina of ethmoid bone
References
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 155 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
External links
- Anatomy photo:29:st-0201 at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center - "Orbits and Eye: Bones"
- "Anatomy diagram: 34256.000-2". Roche Lexicon - illustrated navigator. Elsevier. Archived from the original on 2014-01-01.