Occipital bun
An occipital bun is a prominent bulge or projection of the occipital bone at the back of the skull. It is important in scientific descriptions of classic Neanderthal crania. While common among many of humankind's ancestors, primarily robust relatives rather than gracile, the protrusion is rare in modern Homo sapiens.

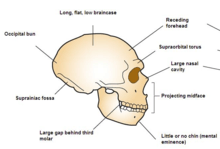

It is suspected that occipital buns might correlate with the biomechanics of running. Another as yet unsubstantiated theory attributes them to enlargement of the cerebellum, a region of the brain which mediates the timing of motor actions and spatial reasoning.
There are still some human populations which often exhibit occipital buns. A greater proportion of early modern Europeans had them, but prominent occipital buns in modern populations are now relatively infrequent.
A study conducted by Lieberman, Pearson and Mowbray provides evidence that individuals with narrow heads (dolicocephalic) or narrow cranial bases and relatively large brains are more likely to have occipital buns as a means of resolving a spatial packing problem.[1]
References
- Lieberman DE, Pearson OM, Mowbray KM (2000). "Basicranial influence on overall cranial shape". J. Hum. Evol. 38 (2): 291–315. doi:10.1006/jhev.1999.0335. PMID 10656780.
External links
- PBS.org - 'Neanderthals on Trial' (January 22, 2002)