Filibuvir
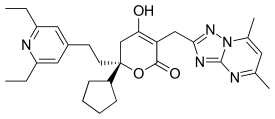
Filibuvir (also known as PF-00868554, PF-868554) was a non-nucleoside orally available[1] NS5B inhibitor developed by Pfizer for the treatment of hepatitis C. It binds to the non-catalytic Thumb II allosteric pocket of NS5B viral polymerase and causes a decrease in viral RNA synthesis. It is a potent and selective inhibitor, with a mean IC50 of 0.019 μM against genotype 1 polymerases.[2] Several filibuvir-resistant mutations have been identified, M423 being the most common that occurred after filibuvir monotherapy.[3] It was intended to be taken twice-daily.[4]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | PF-00868554 |
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| PDB ligand | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C29H37N5O3 |
| Molar mass | 503.636 g/mol g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
Its investigation was discontinued on February 2013 due to strategic reasons.[5][6]
References
- "Pfizer Halts Development of Hepatitis C Drug Filibuvir: Report". FirstWorld Pharma. Doctor's Guide Publishing Limited. Retrieved 5 December 2015.
- Shi, S. T.; Herlihy, K. J.; Graham, J. P.; Nonomiya, J.; Rahavendran, S. V.; Skor, H.; Irvine, R.; Binford, S.; Tatlock, J.; Li, H.; Gonzalez, J.; Linton, A.; Patick, A. K.; Lewis, C. (23 March 2009). "Preclinical Characterization of PF-00868554, a Potent Nonnucleoside Inhibitor of the Hepatitis C Virus RNA-Dependent RNA Polymerase". Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy. 53 (6): 2544–52. doi:10.1128/AAC.01599-08. PMC 2687230. PMID 19307358.
- Jiao, P; Xue, W; Shen, Y; Jin, N; Liu, H (April 2014). "Understanding the Drug Resistance Mechanism of Hepatitis C Virus NS5B to PF-00868554 due to Mutations of the 423 Site: a Computational study". Molecular BioSystems. 10 (4): 767–77. doi:10.1039/c3mb70498j. PMID 24452008.
- Beaulieu, PL (December 2010). "Filibuvir, a Non-nucleoside NS5B polymerase Inhibitor for the Potential Oral Treatment of Chronic HCV Infection". IDrugs: the Investigational Drugs Journal. 13 (12): 938–48. PMID 21154154.
- "Pfizer Stops Developing Hepatitis C Drug". The Wall Street Journal. Dow Jones & Company, Inc. Retrieved 5 December 2015.
- Gentile, Ivan; Buonomo, Antonio Riccardo; Zappulo, Emanuela; Borgia, Guglielmo (February 2015). "Discontinued Drugs in 2012–2013: Hepatitis C Virus Infection". Expert Opinion on Investigational Drugs. 24 (2): 239–51. doi:10.1517/13543784.2015.982274.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative
Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.