Condylostoma
Condylostoma is a genus of unicellular ciliate protists, belonging to the class Heterotrichea.
| Condylostoma | |
|---|---|
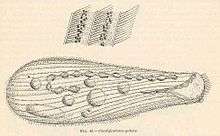 | |
| Condylostoma patens | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| (unranked): | SAR |
| (unranked): | |
| Phylum: | Ciliophora |
| Subphylum: | |
| Class: | |
| Family: | Condylostomatidae |
| Genus: | Condylostoma Bory de Saint Vincent, 1826 |
Species list
According to the World Register of Marine Species, genus Condylostoma contains 24 species:[1]
- Condylostoma acuta Dragesco, 1954
- Condylostoma ancestralis Villeneuve-Brachon, 1940
- Condylostoma arenarium Spiegel, 1926
- Condylostoma caudatum Lauterborn, 1908
- Condylostoma curva Burkovsky, 1970
- Condylostoma enigmatica Dragesco, 1954
- Condylostoma fjeldi Hartwig, 1973
- Condylostoma granulosum Bullington, 1940
- Condylostoma kahli Dragesco, 1960
- Condylostoma magnum Spiegel, 1926
- Condylostoma minima Dragesco, 1960
- Condylostoma minutum Bullington, 1940
- Condylostoma nigra Dragesco, 1960
- Condylostoma patens O.F. Müller, 1786
- Condylostoma patulum Claparède & Lachmann, 1858
- Condylostoma psammophilum Bock, 1952
- Condylostoma remanei Spiegel, 1928
- Condylostoma rugosa Kahl, 1928
- Condylostoma spatiosum Ozaki & Yagiu in Yagiu, 1944
- Condylostoma subterraneum Lepsi, 1964
- Condylostoma tardum Penard, 1922
- Condylostoma tenuis Faure-Fremiet, 1958
- Condylostoma vastum Bock, 1955
- Condylostoma vorticella Ehrenberg, 1833
Phylogeny
Molecular analyses based on either a single locus (small subunit rRNA) or several loci (SSU rDNA, large subunit rRNA, ITS1-5.8S-ITS2 region, alpha-tubulin and COI) showed that Condylostoma is phylogenetically related to the genera Condylostentor and Chattonidium, and with Condylostomides possibly being their sister-group.[2][3][4]
Alternative genetic code
An alternative genetic code is used by the nuclear genome of Condylostoma magnum.[5] This code corresponds to translation table 28 and involves the unusual reassignment of the three standard termination codons to sense codons:
UAAintoGln (Q)orTermination (*);UAGintoGln (Q)orTermination (*);UGAintoTrp (W)orTermination (*).
References
- "WoRMS - World Register of Marine Species - Condylostoma Bory de St. Vincent, 1824". www.marinespecies.org. Retrieved 2017-01-20.
- Guo, Wenbo; Song, Weibo; Al-Rasheid, Khaled A. S.; Shao, Chen; Miao, Miao; Al-Farraj, Saleh A.; Al-Qurishy, Saleh A.; Chen, Zigui; Yi, Zhenzhen (2008-09-10). "Phylogenetic position of three Condylostoma species (Protozoa, Ciliophora, Heterotrichea) inferred from the small subunit rRNA gene sequence". Progress in Natural Science. 18 (9): 1089–1093. doi:10.1016/j.pnsc.2008.04.003.
- Yan, Ying; Chen, Xumiao; Chen, Xiangrui; Gao, Feng; Al-Farraj, Saleh A.; Al-Rasheid, Khaled A. S. (2015-02-01). "Morphology and molecular phylogeny of three marine Condylostoma species from China, including two new ones (Ciliophora, Heterotrichea)". European Journal of Protistology. 51 (1): 66–78. doi:10.1016/j.ejop.2014.11.001.
- Fernandes, Noemi M.; Paiva, Thiago da Silva; da Silva-Neto, Inácio D.; Schlegel, Martin; Schrago, Carlos G. (2016-02-01). "Expanded phylogenetic analyses of the class Heterotrichea (Ciliophora, Postciliodesmatophora) using five molecular markers and morphological data". Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution. 95: 229–246. doi:10.1016/j.ympev.2015.10.030.
- Heaphy, Stephen M.; Mariotti, Marco; Gladyshev, Vadim N.; Atkins, John F.; Baranov, Pavel V. (2016-11-01). "Novel Ciliate Genetic Code Variants Including the Reassignment of All Three Stop Codons to Sense Codons in Condylostoma magnum". Molecular Biology and Evolution. 33 (11): 2885–2889. doi:10.1093/molbev/msw166. hdl:10468/3302. ISSN 0737-4038. PMC 5062323. PMID 27501944.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative
Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.