Ancyromonadida
Ancyromonadida or Planomonadida is a small group of biflagellated protists found in the soil and in aquatic habitats, where they feed on bacteria.[1][2] Includes freshwater or marine organisms, benthic, dorsoventrally compressed and with two unequal flagellae, each emerging from a separate pocket. The apical anterior flagellum can be very thin or end in the cell membrane, while the posterior flagellum is long and is inserted ventrally or laterally. The cell membrane is supported by a thin single layer teak and the mitochondrial crests are discoidal / flat.[3]
| Ancyromonadida | |
|---|---|
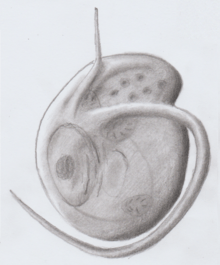 | |
| Ancyromonas | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Phylum: | |
| Order: | Ancyromonadida Cavalier-Smith 1997 emend. Atkins 2000 |
|
Family
| |
| Synonyms | |
| |
The group's placement is doubtful, as it seems to fall outside the five supergroups of Eukarya.[4] Cavalier-Smith considers that they constitute a basal group to Amoebozoa and Opisthokonta and places it together with other related groups in Sulcozoa.[5] However, they appear more basal than Malawimonas, placing them in Loukouzoa, possibly as stem podiates, and depending on the placement of the root position of the Eukaryotes.[6][7]
Taxonomy
- Order Ancyromonadida Cavalier-Smith 1998 emend. Atkins 2000[8]
- Family Ancyromonadidae Cavalier-Smith 1993
- Genus Ancyromonas Kent 1880
- Species A. abrupta Skvortzov 1957
- Species A. contorta (Klebs 1883) Lemmermann
- Species A. lata Skvortzov 1957
- Species A. magna Zhang & Yang 1993
- Species A. metabolica Skvortzov 1957
- Species A. nitzschiae Skvortzov 1957
- Species A. parasitica Massart
- Species A. prima Skvortzov1957
- Species A. rotundata Skvortzov 1957
- Species A. rugosa Skvortzov 1957
- Species A. ruminantium Certes 1899
- Species A. socialis Skvortzov 1957
- Species A. sigmoides Kent 1880 sensu Heiss, Walker & Simpson 2010
- Genus Ancyromonas Kent 1880
- Family Planomonadidae Cavalier-Smith 2008
- Genus Fabomonas Glücksman & Cavalier-Smith 2013
- Species Fabomonas tropica Glücksman & Cavalier-Smith 2013
- Genus Planomonas Cavalier-Smith 2008 emend. Cavalier-Smith 2013
- Species P. melba (Simpson & Patterson 1996) Cavalier-Smith 2008 [Ancyromonas melba Patterson & Simpson 1996]
- Species P. brevis Glücksman & Cavalier-Smith 2013
- Species P. bulbosa Glücksman & Cavalier-Smith 2013
- Species P. elongata Glücksman & Cavalier-Smith 2013
- Species P. micra Cavalier-Smith 2008 [Ancyromonas micra (Cavalier-Smith 2008) Heiss, Walker & Simpson 2010]
- Genus Fabomonas Glücksman & Cavalier-Smith 2013
- Family Nutomonadidae Cavalier-Smith 2013
- Genus Nutomonas Cavalier-Smith 2013
- Species N. sinistra (Cavalier-Smith 2008) Cavalier-Smith 2013 [Ancyromonas sinistra (Cavalier-Smith 2008) Al-Qassab et al. 2002; Planomonas sinistra Cavalier-Smith 2008]
- Subgenus (Striomonas) Cavalier-Smith 2013
- Species N. longa Cavalier-Smith & Glücksman 2013 [N. (Incisomonas) longa Cavalier-Smith 2013]
- Subgenus (Kentomonas) Cavalier-Smith 2013
- Species N. atlantica Glücksman & Cavalier-Smith 2013 [Ancyromonas atlantica]
- Species N. indica Glücksman & Cavalier-Smith 2013 [Ancyromonas indica]
- Species N. mylnikovi (Cavalier-Smith 2008) Cavalier-Smith 2013 [Planomonas mylnikovi Cavalier-Smith 2008]
- Species N. kenti Cavalier-Smith 2013 [Ancyromonas kenti]
- Subgenus (Nutomonas) Cavalier-Smith 2013
- Species N. howeae (Cavalier-Smith 2008) Glücksman & Cavalier-Smith 2013 [Ancyromonas howeae (Cavalier-Smith 2008) Heiss, Walker & Simpson 2010; Planomonas howeae Cavalier-Smith 2008]
- Subspecies N. h. howeae (Cavalier-Smith 2008) Glücksman & Cavalier-Smith 2013
- Subspecies N. h. lacustris Glücksman & Cavalier-Smith 2013
- Species N. limna (Cavalier-Smith 2008) Glücksman & Cavalier-Smith 2013 [Ancyromonas limna (Cavalier-Smith 2008) Heiss, Walker & Simpson 2010; Planomonas limna Cavalier-Smith 2008]
- Subspecies N. l. limna (Cavalier-Smith 2008) Glücksman & Cavalier-Smith 2013
- Subspecies N. l. terrestris Cavalier-Smith & Glücksman 2013
- Species N. howeae (Cavalier-Smith 2008) Glücksman & Cavalier-Smith 2013 [Ancyromonas howeae (Cavalier-Smith 2008) Heiss, Walker & Simpson 2010; Planomonas howeae Cavalier-Smith 2008]
- Genus Nutomonas Cavalier-Smith 2013
- Family Ancyromonadidae Cavalier-Smith 1993
References
- Cavalier-Smith, T. (2013). Early evolution of eukaryote feeding modes, cell structural diversity, and classification of the protozoan phyla Loukozoa, Sulcozoa, and Choanozoa. European journal of protistology, 49(2), 115-178.
- Cavalier-Smith T, Chao EE, Stechmann A, Oates B, Nikolaev S (October 2008). "Planomonadida ord. nov. (Apusozoa): ultrastructural affinity with Micronuclearia podoventralis and deep divergences within Planomonas gen. nov". Protist. 159 (4): 535–62. doi:10.1016/j.protis.2008.06.002. PMID 18723395.
- Adl, Sina M.; Simpson, Alastair G. B.; Lane, Christopher E.; Lukeš, Julius; Bass, David; Bowser, Samuel S.; Brown, Matthew W.; Burki, Fabien; Dunthorn, Micah; Hampl, Vladimir; Heiss, Aaron; Hoppenrath, Mona; Lara, Enrique; Le Gall, Line; Lynn, Denis H.; McManus, Hilary; Mitchell, Edward A. D.; Mozley-Stanridge, Sharon E.; Parfrey, Laura W.; Pawlowski, Jan; Rueckert, Sonja; Shadwick, Laura; Schoch, Conrad L.; Smirnov, Alexey; Spiegel, Frederick W. (2012). "The Revised Classification of Eukaryotes". Journal of Eukaryotic Microbiology. 59 (5): 429–514. doi:10.1111/j.1550-7408.2012.00644.x. PMC 3483872. PMID 23020233.
- Burki, F. (2014). "The eukaryotic tree of life from a global phylogenomic perspective". Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Biology. 6 (5): 1–17. doi:10.1101/cshperspect.a016147. PMC 3996474. PMID 24789819.
- Ruggiero, M. A., Gordon, D. P., Orrell, T. M., Bailly, N., Bourgoin, T., Brusca, R. C., Cavalier-Smith, T., Guiry, M.D. y Kirk, P. M. (2015). A Higher Level Classification of All Living Organisms.
- Brown, Matthew W.; Heiss, Aaron; Kamikawa, Ryoma; Inagaki, Yuji; Yabuki, Akinori; Tice, Alexander K.; Shiratori, Takashi; Ishida, Ken; Hashimoto, Tetsuo (2017-12-03). "Phylogenomics places orphan protistan lineages in a novel eukaryotic super-group". bioRxiv. 10 (2): 427–433. doi:10.1101/227884. PMC 5793813. PMID 29360967.
- Torruella, Guifré; Mendoza, Alex de; Grau-Bové, Xavier; Antó, Meritxell; Chaplin, Mark A.; Campo, Javier del; Eme, Laura; Pérez-Cordón, Gregorio; Whipps, Christopher M. (2015). "Phylogenomics Reveals Convergent Evolution of Lifestyles in Close Relatives of Animals and Fungi". Current Biology. 25 (18): 2404–2410. doi:10.1016/j.cub.2015.07.053. PMID 26365255.
- Glücksman, Snell & Cavalier-Smith (2013). "Phylogeny and evolution of Planomonadida (Sulcozoa): Eight new species and new genera Fabomonas and Nutomonas". European Journal of Protistology. 49 (2): 179–200. doi:10.1016/j.ejop.2012.08.007. PMID 23369787.
External links
| Wikispecies has information related to Ancyromonadida |