What Everyone Should Know
Español: Lo que todos deben saber
Antibiotic resistance is a growing problem, both in the United States and across the world. The main driving factors behind antibiotic resistance are the overuse and misuse of antibiotics. Learn more below about when antibiotics are and are not needed for common infections, and the potential harms of using antibiotics.
If You Have a Cold or Flu, Antibiotics Won’t Work for You
Are you aware that colds, flu, most sore throats, bronchitis, and many sinus and ear infections are caused by viruses? Did you know that antibiotics do not help fight viruses? It’s true. For the overwhelming majority of common respiratory infections, antibiotics are not helpful.
Get Smart…Read the Chart! [1 page] to know which common illnesses are usually viral or bacterial and when antibiotics are necessary.
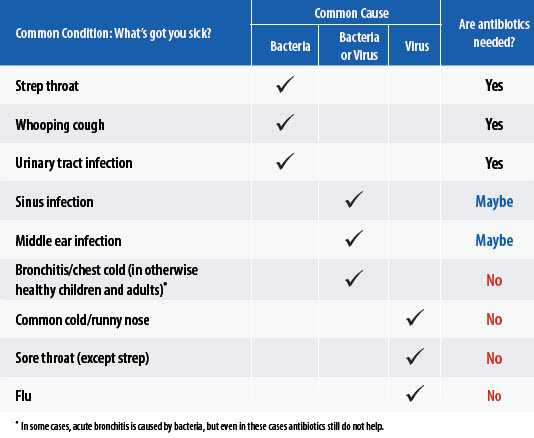
Antibiotics cure bacterial infections, not viral infections such as:
- Colds or flu
- Most coughs and bronchitis
- Most sore throats
- Runny noses
Taking antibiotics for viral infections will not:
- Cure the infection
- Keep other individuals from catching the illness
- Help you feel better
Antibiotics Can Cause More Harm than Good
Taking antibiotics when you have a virus may do more harm than good:

- Taking antibiotics increases your risk of getting an antibiotic-resistant infection later.
- Antibiotics kill the healthy bacteria in the gut, allowing more harmful bacteria, such as C. difficile, to grow in its place.
- Although this infection is more commonly found in hospitals, it also occurs in clinics outside of the hospital. Read more about C. difficile.
- Antibiotics cause 1 out of 5 emergency department visits for adverse drug events.
- Antibiotics are the most common cause of emergency department visits for adverse drug events in children under 18 years of age.
It’s important to only take antibiotics for bacterial infections since they can put you or your child at risk for harmful side effects and antibiotic-resistant infections.
- Page last reviewed: February 1, 2017
- Page last updated: February 1, 2017
- Content source:


 ShareCompartir
ShareCompartir