Sore Throat
Español: Dolor de garganta
Overview
Most sore throats will go away on their own without antibiotics. In some cases (like for strep throat), a lab test will need to be done to see if you or your child need antibiotics.
Causes
Most sore throats are caused by viruses, like ones that cause a cold or the flu, and do not need antibiotic treatment.
Some sore throats are caused by bacteria, such as group A Streptococcus (group A strep). Sore throats caused by these bacteria are known as strep throat. In children, 20 to 30 out of every 100 sore throats are strep throat. In adults, only 5 to 15 out of every 100 sore throats is strep throat.
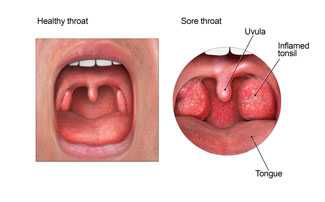 View larger image
View larger image
When you have a sore throat, your tonsils often hurt and are usually red and swollen.
Other common causes of sore throats include:
- Allergies
- Dry air
- Pollution (airborne chemicals or irritants)
- Smoking or exposure to second-hand smoke
Risk Factors
There are many things that can increase your risk for a sore throat, including:
- Age (children and teens between 5 and 15 years old are most likely to get a sore throat)
- Exposure to someone with a sore throat or strep throat
- Time of year (winter and early spring are common times for strep throat)
- Weather (cold air can irritate your throat)
- Irregularly shaped or large tonsils
- Pollution or smoke exposure
- A weak immune system or taking drugs that weaken the immune system
- Post-nasal drip or allergies
- Acid reflux disease
Signs and Symptoms
A sore throat can make it painful to swallow. A sore throat can also feel dry and scratchy, and may be a symptom of the common cold or other upper respiratory tract infection.
The following symptoms are often associated with sore throats caused by a viral infection or due to allergies:
- Sneezing
- Coughing
- Watery eyes
- Mild headache or body aches
- Runny nose
- Low fever (less than 101 °F)
Symptoms more commonly associated with strep throat include:
- Red and swollen tonsils, sometimes with white patches or streaks of pus
- Tiny red spots (petechiae) on the soft or hard palate (the roof of the mouth)
- High fever (101 °F or above)
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Swollen lymph nodes in the neck
- Severe headache or body aches
- Rash
When to Seek Medical Care
See a healthcare professional if you or your child has any of the following:
- Sore throat that lasts longer than 1 week
- Difficulty swallowing or breathing
- Excessive drooling (young children)
- Temperature higher than 100.4 °F
- Pus on the back of the throat
- Rash
- Joint pain
- Hoarseness lasting longer than 2 weeks
- Blood in saliva or phlegm
- Dehydration (symptoms include a dry, sticky mouth; sleepiness or tiredness; thirst; decreased urination or fewer wet diapers; few or no tears when crying; muscle weakness; headache; dizziness or lightheadedness)
- Recurring sore throats
If your child is younger than three months of age and has a fever, it’s important to always call your healthcare professional right away.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Antibiotics are not needed to treat most sore throats, which usually improve on their own within 1–2 weeks. Antibiotics will not help if a sore throat is caused by a virus or irritation from the air. Antibiotic treatment in these cases may cause harm in both children and adults. Your healthcare professional may prescribe other medicine or give you tips to help with other symptoms like fever and coughing.
Antibiotics are needed if a healthcare professional diagnoses you or your child with strep throat, which is caused by bacteria. This diagnosis can be done using a quick swab of the throat. Strep throat cannot be diagnosed by looking in the throat—a lab test must be done.
Antibiotics are prescribed for strep throat to prevent rheumatic fever. If diagnosed with strep throat, an infected patient should stay home from work, school, or day care until 24 hours after starting an antibiotic.
Symptom Relief
Rest, over-the-counter medicines and other self-care methods may help you or your child feel better. For more information about symptomatic relief, visit the Symptom Relief section of this website or talk to your healthcare professional, including your pharmacist. Remember, always use over-the-counter products as directed. Many over-the-counter products are not recommended for children of certain ages.
Prevention
There are steps you can take to help prevent getting a sore throat, including:
- Practice good hand hygiene
- Avoid close contact with people who have sore throats, colds or other upper respiratory infections
- Avoid smoking and exposure to secondhand smoke
- Page last reviewed: April 17, 2015
- Page last updated: July 23, 2015
- Content source:


 ShareCompartir
ShareCompartir