کوکین
کوکین ایک طاقتور اور مہنگا نشہ ہے۔ اسے کوکا نامی درخت سے حاصل کیا جاتا ہے۔ یہ کئی قسموں، جسے سفید پاؤڈر، پیسٹ (آمیزے) یا پتھر(کرسٹل) کی صورت میں ملتا ہے۔اسے ناک سے سونگھا جاتا ہے، مسوڑوں پر ملا جاتا ہے یا انجیکشن کی مدد سے رگوں میں انجیکٹ کیا جاتا ہے، جس کے بعد یہ فوری طور پر انسان کو راحت پہنچانے والے دماغی حصے کو فعال کردیتی ہے۔
 | |
 | |
| طبی معلومات | |
|---|---|
| تجارتی نام | Psicaine, Delcaine, Ensan Cocaine[حوالہ درکار] |
| اے ایچ ایف ایس/Drugs.com | Micromedex Detailed Consumer Information |
| حمل زمرہ |
|
| انحصار ذمہ داری | |
| لت ذمہ داری | High[3] |
| راستے | Topical، عطائی راستہ، insufflation، intravenous |
| Drug class |
|
| اے ٹی سی رمز | |
| قانونی حیثیت | |
| قانونی حیثیت |
|
| دوا کے جزب و تقسیم کے مطالعہ کی معلومات | |
| حیاتی اثر پذیری | |
| تحول | جگر CYP3A4 |
| Onset of action | seconds to minutes[9] |
| Biological half-life | 1 hour |
| Duration of action | 5 to 90 minutes[9] |
| Excretion | Kidney |
| شناخت کنندہ | |
|
آئی یو پی اے سی نام
| |
| مترادفات | Benzoylmethylecgonine, coke |
| سی اے ایس نمبر | |
| پبکیم CID | |
| آئی یو پی ایچ اے آر/بی پی ایس | |
| ڈرگ بنک | |
| کیم اسپائڈر | |
| یو این آئی آئی | |
| کے ای جی جی |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| پی ڈی بی ligand | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.030 |
| کیمیائی و طبعی معلومات | |
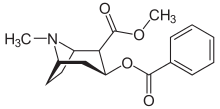
| فارمولا | C17H21NO4 |
| مولر کمیت | 303.353 g/mol |
| سہ رخی ماڈل (Jmol) | |
| نقطۂ پگھلاؤ | 98 °C (208 °F) |
| نقطہ کھولاؤ | 187 °C (369 °F) |
| پانی میں حل پذیری | ~1.8 mg/mL (20 °C) |
| |
|
InChI
| |
| | |
مزید دیکھیے
حوالہ جات
- RC Malenka، EJ Nestler، SE Hyman۔ "Chapter 15: Reinforcement and Addictive Disorders"۔ بہ A Sydor، RY Brown۔ Molecular Neuropharmacology: A Foundation for Clinical Neuroscience (اشاعت 2nd۔)۔ New York: McGraw-Hill Medical۔ صفحہ 367۔ آئی ایس بی این 978-0-07-148127-4۔
While physical dependence and withdrawal occur with some drugs of abuse (opiates, ethanol)، these phenomena are not useful in the diagnosis of addiction because they do not occur with other drugs of abuse (cocaine, amphetamine) and can occur with many drugs that are not abused (propranolol, clonidine)۔
- Hamid Ghodse (2010)۔ Ghodse's Drugs and Addictive Behaviour: A Guide to Treatment (اشاعت 4۔)۔ Cambridge University Press۔ صفحہ 91۔ آئی ایس بی این 978-1-139-48567-8۔ مورخہ 10 ستمبر 2017 کو اصل سے آرکائیو شدہ۔
- Introduction to Pharmacology Third Edition۔ Abingdon: CRC Press۔ 2007۔ صفحات 222–223۔ آئی ایس بی این 978-1-4200-4742-4۔
- "DEA / Drug Scheduling"۔ www.dea.gov۔ مورخہ 9 اگست 2017 کو اصل سے آرکائیو شدہ۔ اخذ شدہ بتاریخ 7 اگست 2017۔
- "Nasal mucosal versus gastrointestinal absorption of nasally administered cocaine". Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 56 (4): 305–10. 2000. doi:. PMID 10954344.
- "Cocaine pharmacokinetics in humans". J Ethnopharmacol 3 (2–3): 353–66. 1981. doi:. PMID 7242115.
- "Cocaine disposition in humans after intravenous injection, nasal insufflation (snorting)، or smoking". Drug Metab. Dispos. 17 (2): 153–9. 1989. PMID 2565204.
- "Intranasal and oral cocaine kinetics". Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 27 (3): 386–94. 1980. doi:. PMID 7357795.
بیرونی روابط
| ویکی اقتباس میں کوکین سے متعلق اقتباسات موجود ہیں۔ |
| ویکی کومنز پر کوکین سے متعلق سمعی و بصری مواد ملاحظہ کریں۔ |
| cocaine کے لغوی معنوں کے لئے ویکی لغت میں دیکھیے۔ |
سانچہ:Euphoriants سانچہ:Stimulants سانچہ:Local anesthetics
سانچہ:Ion channel modulators سانچہ:Monoamine reuptake inhibitors سانچہ:Sigma receptor modulators
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative
Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.