سکھ گرو
سکھ گروؤں نے سکھ مذہب قائم کیا جس کی ابتدا تقریباً 1469ء میں ہوئی۔[1] گرو نانک سکھوں کے پہلے تسلیم شدہ گرو ہیں۔[2]

گرو نانک کے سلسلہ میں دس گرووں کو تسلیم کیا جاتا ہے۔ جدید سکھ مذہب میں گرووں کی تحریروں گرنتھ صاحب کو بھی گرو مانا جاتا ہے۔ اس عقیدہ کے تحت گروؤں کی تحریروں کو اب گرو گرنتھ صاحب کہا جاتا ہے۔ جدید سکھ مت کے مطابق دسویں گرو گرو گوبند سنگھ نے سلسلہ گرو ہمیشہ کے لیے گرو گرنتھ صاحب کو عطا کر دیا ہے۔
گرو کی خصوصیات
گرو نانک کے مطابق کوئی بھی شخص گرو یعنی استاد کامل کے بغیر خدا کو نہیں پا سکتا۔ گرو اس کے دل سے غرور اور دنیاوی محبت نکالتا اور اعلٰی ترین صداقت سے روشناس کرواتا ہے۔ ”سچا گرو“ علم کی تلوار کا مالک ہوتا ہے اور دل کے ساتھ لڑتا ہے۔ وہ دس اعضاء کے فعل اور فعل راز اور تمام برے جذبات کو جانتا ہے۔ وہ الوہی علم میں کامل اور غرور و خود فریبی سے آزاد ہوتا ہے۔ اس کا دل دنیاوی خواہشات سے پاک ہوتا ہے۔ وہ نفس کش ہوتا، کم سوتا اور بہت کم کھاتا ہے۔ وہ اپنے متبرک جسم کی حفاظت کرتا ہے۔ وہ بھگتی اور ریاضت میں مستحکم ہوتا ہے۔ وہ دن رات الوہی علم بتاتا ہے۔ وہ غرق خدا ہو کر بیدا ہوتا ہے۔
فہرست
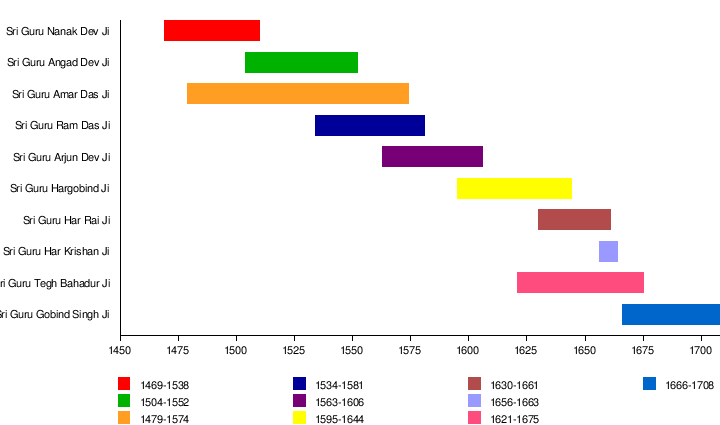
| # | نام | تاریخ پیدائش | کرو کے مرتبہ پر فائز | تاریخ وفات | وفات پر عمر | زندگی کی اہم جھلکیاں | والد | والدہ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | گرو نانک | 15 اپریل 1469ء | -- | 22 ستمبر 1539ء | 69 | [3] | مہتا کالو | ماتا ترپتا |
| 2 | گرو انگد دیو | 31 مارچ 1504ء | 7 ستمبر 1539ء | 29 مارچ 1552ء | 48 | [4] | بابا پھیرو | ماتا رامو |
| 3 | گرو امر داس | 5 مئی 1479ء | 26 مارچ 1552ء | 1 ستمبر 1574ء | 95 | [5] | تیج بھان بھلا | بخت کور |
| 4 | گرو رام داس | 24 ستمبر 1534ء | 1 ستمبر 1574ء | 1 ستمبر 1581ء | 46 | [6] | بابا ہری داس | ماتا دیا وتی |
| 5 | گرو ارجن دیو | 15 اپریل 1563ء | 1 ستمبر 1581ء | 30 مئی 1606ء | 43 | [7] | رام داس | ماتا بھانی |
| 6 | گرو ہرگوبند | 19 جون 1595ء | 25 مئی 1606ء | 28 فروری 1644ء | 48 | [8] | ارجن دیو | ماتا گنگا |
| 7 | گرو ہررائے | 16 جنوری 1630ء | 3 مارچ 1644ء | 6 اکتوبر 1661ء | 31 | [9] | بابا گردتا | ماتا نہال کور |
| 8 | گرو ہرکرشن | 7 جولائی 1656ء | 6 اکتوبر 1661ء | 30 مارچ 1664ء | 7 | [10] | ہری رائے | ماتا کرشن کور |
| 9 | گرو تیغ بہادر | 1 اپریل 1621ء | 20 مارچ 1665ء | 11 نومبر 1675ء | 54 | [11] | ہری گوبند | ماتا نانکی |
| 10 | گرو گوبند سنگھ | 22 دسمبر 1666ء | 11 نومبر 1675ء | 7 اکتوبر 1708ء | 41 | [12] | تیغ بہادر | ماتا گجری |
| 11 | گرو گرنتھ صاحب | نا معلوم | 7 اکتوبر 1708ء | نا معلوم | نا معلوم | حتمی اور آخری، دائمی زندہ گرو | - | - |
حوالہ جات
- Sailendra Sen۔ A Textbook of Medieval Indian History۔ Primus Books۔ صفحات 186–187۔ آئی ایس بی این 978-9-38060-734-4۔
- Shiromani Gurdwara Prabandhak Committee. "Ten Gurus"
-
- Founded سکھ مت * Spiritual revelations registered as 974 hymns in گرنتھ صاحب * Rejected the authority of the وید * Preached the new idea of God as (Supreme, Universal, All-powerful and truthful, Formless, Fearless, Without Hate, Self-existent, Ever-lasting creator of all things, The eternal and absolute truth) * Attacked the citadel of the Hindu caste system, promoting equality of all * Emphasized the equality of women *Rejected the path of renunciation; emphasized leading a householder's life * Condemned the theocracy of Mughal emperor Babar * Started the institution of Guru ka Langar * Undertook 4 major journeys, travelling far and wide (including visits to Haridwar, Varanasi, Tibet, Srinagar, Lahore, Mecca, Medina, Baghdad, Syria, Turkey, Kabul, Kandhar, etc.) * Died of natural causes
-
- Spiritual revelations registered as 63 Saloks (stanzas) in گرنتھ صاحب * Established new religious institutions to strengthen the base of Sikhism * Standardized and popularized the گرمکھی Script* Opened many new schools * Started the tradition of Mall Akhara for physical as well as spiritual development * Popularized and expanded the institution of Guru ka Langar * Died of natural causes
-
- 869 verses including Anand Sahib in the گرنتھ صاحب * Established Manji & Piri system of religious missions for men and women respectively * Strengthened the Langar community kitchen system * Preached against the Hindu society's Sati system (burning alive of a wife at the pyre of her deceased husband), advocated widow-remarriage; Asked the women to discard "Purdah" (veil worn by Muslim women). * Asked جلال الدین اکبر to remove the toll-tax (pilgrim's tax) for non-Muslims while crossing Yamuna and Ganges Rivers * Died of natural causes
-
- 638 hymns in 30 ragas in the گرنتھ صاحب, which include 246 Padei, 138 Saloks, 31 Ashtpadis and 8 Vars * Composed the four Lawans (stanzas) of the Anand Karaj, a distinct marriage code for سکھs separate from the orthodox and traditional Hindu Vedi system* Laid the foundation stone of Chak Ramdas or Ramdas Pur, now called Amritsar * Strongly decried superstitions, caste system and pilgrimages *Died of natural causes
-
- Compiled the گرنتھ صاحب, and installed it at Sri Harmandir Sahib on Bhadon Sudi 1st Samvat 1661 (August/ستمبر 1604), A landmark event in Sikh history* Contributed about 2000 verses to the گرنتھ صاحب * Founded the town of Tarn Taran Sahib near Goindwal Sahib * Built a house for Lepers. * Was tortured and executed on the orders of the Mughal Emperor نورالدین جہانگیر * Hailed as the first martyr of Sikh religion, and as Shaheedan-de-Sartaj (The crown of martyrs)
-
- Instituted the practice of maintaining armed legion of سکھ warrior-saints * Waged wars against rulers نورالدین جہانگیر and شاہجہان * Died of natural causes
-
- Sheltered داراشکوہ; persecuted by اورنگزیب عالمگیر who framed charges of anti-Islamic blasphemy against Guru Ji and Sikh verses of گرنتھ صاحب * Died of natural causes
-
- Forcibly summoned to دہلی (the imperial capital of اورنگزیب عالمگیر) under framed charges * Died of the age of 8 due to smallpox, which he contracted while healing the sick people during an epidemic.
-
- Opposed the forced conversions of the Hindu کشمیری پنڈتs by مسلمانs * Was consequently persecuted, imprisoned, tortured and executed under the orders of the Mughal emperor اورنگزیب عالمگیر. Contributed many hymns (Shlokas) to گرنتھ صاحب * Spread Sikhism far and wide to بہار (بھارت) and آسام *
-
- Founded خالصہ in 1699 * Last Sikh Guru in human form * Passed the Guruship of the Sikhs to the گرنتھ صاحب * Died of complications from stab wounds inflicted by پشتون assassins sent by فہرست حکمران مغلیہ سلطنت governor Wazir Khan