Tripterygium wilfordii
Tripterygium wilfordii, or léi gōng téng (Mandarin) (Chinese:雷公藤, Japanese: raikōtō), sometimes called thunder god vine but more properly translated thunder duke vine, is a vine used in traditional Chinese medicine.
| Tripterygium wilfordii | |
|---|---|
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Clade: | Rosids |
| Order: | Celastrales |
| Family: | Celastraceae |
| Genus: | Tripterygium |
| Species: | T. wilfordii |
| Binomial name | |
| Tripterygium wilfordii Hook.f. | |
Tripterygium wilfordii has been promoted for use in rheumatoid arthritis and psoriasis; however, due to safety concerns this use is not recommended.[1] Evidence is insufficient to deem it effective as a method of birth control.[2]
Health effects
The United Kingdom government does not recommend the use of Tripterygium due to potential side effects.[1]
Birth control
Evidence is lacking that Tripterygium is either safe or effective as a method of birth control in men.[2] Two trials found less sperm in people taking it for rheumatoid arthritis but these trials were observational in nature.[2]
Rheumatoid arthritis
In China, T. wilfordii has historically been used as a treatment of rheumatoid arthritis (RA). The National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health has noted tentative evidence that T. wilfordii may improve some RA symptoms.[3] Serious side effects, however, occur frequently enough to make the risks of taking it higher than the possible benefits.[3]
Side effects
At medicinal doses, T. wilfordii extract can have significant side effects,[3] including immunosuppression.
In August 2011, the UK Medicines and Healthcare Products Regulatory Agency published a drug safety bulletin advising consumers not to use medicines containing lei gong teng due to potentially serious side effects.[4]
China State Food and Drug Administration issued a warning in April 2012 about this medicine, urging caution.[5]
A 2016 review found gastrointestinal symptoms in 13%, adverse reproductive outcomes in 12%, adverse skin reactions in 8%, hematologic events in 6.5%, cardiovascular events in 5%. Also irregular menstruation OR=4.6.[6]
A 2011 review stated that although T. wilfordii has toxic potential, careful extraction gives an acceptable frequency of adverse reactions, which are largely related to the gastrointestinal tract and amenorrhea. The review found that T. wilfordii extract is useful remedy for postmenopausal rheumatoid arthritis.[7]
Pharmacology
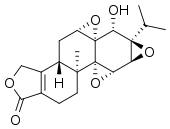
Celastrol, a pentacyclic triterpenoid, and triptolide, a diterpene triepoxide, are putative active components of the extracts derived from Tripterygium wilfordii. Triptolide has pharmacological activities including anti-inflammatory, immune modulation, antiproliferative, and proapoptotic activity, but its clinical use is limited by severe toxicity.[8]
Footnotes
- "Traditional Chinese medicines containing lei gong teng (tripterygium wilfordii) Drug Safety Update". www.gov.uk. 8 August 2011. Retrieved 10 June 2016.
- Lopez, LM; Grimes, DA; Schulz, KF (November 2005). "Nonhormonal drugs for contraception in men: a systematic review". Obstetrical & Gynecological Survey. 60 (11): 746–52. doi:10.1097/01.ogx.0000182905.71077.13. PMID 16250923.
- "Rheumatoid Arthritis and Complementary Health Approaches". National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health. Retrieved 21 April 2013.
- Drug Safety Update: Traditional Chinese medicines containing lei gong teng (tripterygium wilfordii)
- 中医・我が愛しの上海へ/理想の中医学・漢方を求めて-
- Zhang, C; Sun, PP; Guo, HT; Liu, Y; Li, J; He, XJ; Lu, AP (8 November 2016). "Safety Profiles of Tripterygium wilfordii Hook F: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis". Frontiers in Pharmacology. 7: 402. doi:10.3389/fphar.2016.00402. PMC 5099241. PMID 27877128.
- Bao J.; Dai S.-M. (September 2011). "A Chinese herb Tripterygium wilfordii Hook F in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis: Mechanism, efficacy, and safety". Rheumatology International. 31 (9): 1123–1129. doi:10.1007/s00296-011-1841-y. PMID 21365177.
- Liu, Qiuyan (2011). "Triptolide and its expanding multiple pharmacological functions". International Immunopharmacology. 11 (3): 377–383. doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2011.01.012. PMID 21255694.