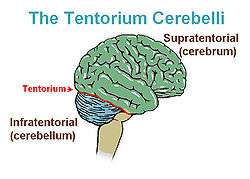
Cerebellar tentorium
The cerebellar tentorium or tentorium cerebelli (Latin for "tent of the cerebellum") is an extension of the dura mater that separates the cerebellum from the inferior portion of the occipital lobes.
| Cerebellar tentorium | |
|---|---|
 | |
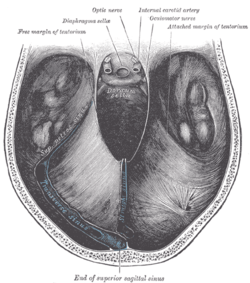 Cerebellar tentorium seen from above. | |
| Details | |
| Part of | Meninges |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | Tentorium cerebelli |
| NeuroNames | 1240 |
| TA | A14.1.01.104 |
| FMA | 83966 |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy | |
Structure
The cerebellar tentorium is an arched lamina, elevated in the middle, and inclining downward toward the circumference.
It covers the top of the cerebellum, and supports the occipital lobes of the brain.
Its anterior border is free and concave, and bounds a large oval opening, the tentorial incisure, for the transmission of the cerebral peduncles.
It is attached, behind, by its convex border, to the transverse ridges upon the inner surface of the occipital bone, and there encloses the transverse sinuses; in front, to the superior angle of the petrous part of the temporal bone on either side, enclosing the superior petrosal sinuses.
At the apex of the petrous part of the temporal bone the free and attached borders meet, and, crossing one another, are continued forward to be fixed to the anterior and posterior clinoid processes (respectively) of the sphenoid bone.
To the middle line of its upper surface the posterior border of the falx cerebri is attached, the straight sinus being placed at their line of junction.
Clinical significance
Brain tumors are often characterized as supratentorial (above the tentorium) and infratentorial (below the tentorium). The location of the tumor can help in determining the type of tumor, as different tumors occur with different frequencies at each location. Additionally, most childhood primary brain tumors are infratentorial, while most adult primary brain tumors are supratentorial. The location of the tumor may have prognostic significance as well.
Since the tentorium is a hard structure, if there is an expansion of the volume of the brain or its surrounding matter above the tentorium, such as because of a tumour or bleeding, the brain can get pushed down partly through the tentorium. This is called herniation and will often cause an enlarged pupil on the affected side, due to pressure on the oculomotor nerve. Tentorial herniation is a serious symptom, especially since the brainstem is likely to be compressed as well if the intracranial pressure rises further. A common type of herniation is uncal herniation.
Calcifications within the cerebellar tentorium are relatively common in elderly people; they seem to rarely cause symptoms.[1]
Additional images
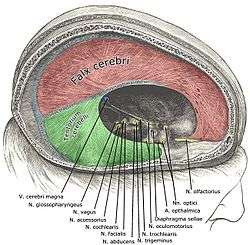 Dura mater and its processes exposed by removing part of the right half of the skull, and the brain.
Dura mater and its processes exposed by removing part of the right half of the skull, and the brain.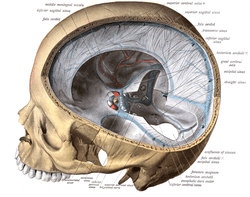 Tentorium cerebelli seen cut out in the back of the skull.
Tentorium cerebelli seen cut out in the back of the skull.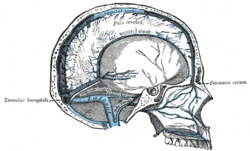 Sagittal section of the skull, showing the sinuses of the dura.
Sagittal section of the skull, showing the sinuses of the dura.- Human brain dura mater (reflections)
 Tentorium cerebelli
Tentorium cerebelli
References
- https://radiopaedia.org/articles/normal-intracranial-calcifications; retrieved 04-07-2018
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 874 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
External links
- Photo at Indiana University
- Atlas image: n2a3p2 at the University of Michigan Health System