Tedizolid
Tedizolid (formerly torezolid, trade name Sivextro),[1] is an oxazolidinone-class antibiotic. Tedizolid phosphate is a phosphate ester prodrug of the active compound tedizolid. It was developed by Cubist Pharmaceuticals, following acquisition of Trius Therapeutics (originator: Dong-A Pharmaceuticals), and is marketed for the treatment of acute bacterial skin and skin structure infections (also known as complicated skin and skin-structure infections (cSSSIs)).[2]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Sivextro |
| Other names | TR-700 |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | Oral, intravenous |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 91% |
| Protein binding | 70–90% |
| Elimination half-life | 12 hours |
| Excretion | Feces |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.249.430 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
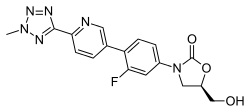
| Formula | C17H15FN6O3 |
| Molar mass | 370.338 g/mol g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| | |
Tedizolid has been approved by the U.S Food and Drug Administration on June 20, 2014, for the treatment of acute bacterial Skin and skin structure infections (ABSSSI) caused by certain susceptible bacteria, including Staphylococcus aureus (including methicillin-resistant strains, MRSA, and methicillin-susceptible strains), various Streptococcus species (S. pyogenes, S. agalactiae, and S. anginosus group including S. anginosus, S. intermedius, and S. constellatus), and Enterococcus faecalis.[3][4] Tedizolid is a second-generation oxazolidinone derivative that is 4-to-16-fold more potent against staphylococci and enterococci compared to linezolid.[5] The recommended dosage for treatment is 200 mg once daily for a total duration of six days, either orally (with or without food) or through an intravenous injection (if patient is older than 18 years old).[4]
Mechanism of action
Tedizolid phosphate (TR-701) is a prodrug activated by plasma or intestinal phosphatases to tedizolid (TR-700) following administration of the drug either orally or intravenously.[4][6] Once activated, tedizolid exerts its bacteriostatic microbial activity through inhibition of protein synthesis by binding to the 50S ribosomal subunit of the bacteria.[4]
Clinical trials
Tedizolid proved its noninferiority to linezolid in two phase-III trials, known as the ESTABLISH trials.[7]
Tedizolid is the second treatment approved by the FDA under the new federal law Generating Antibiotic Incentives Now (known as the GAIN Act).[8][9] New antibiotics manufactured under this new act will be designed as a Qualified Infectious Disease Product (QIDP), allowing an expedited review by the FDA and an additional five years of market exclusivity.[9]
Adverse effects
The most common adverse effects found in the clinical trials were nausea, headache, diarrhea, vomiting, and dizziness.[4] Tedizolid has also been found to have hematologic (blood) effects, as shown in Phase-I studies in which subjects exposed to doses longer than 6 days showed a possible dose and duration effect on hematologic parameters.[4] Its safety in patients with decreased levels of white blood cells has not been established.[3] Patients on tedizolid are also at low risk of peripheral and optic neuropathy, similar to other members of the oxazolidinone class.[4]
References
- "Trius grows as lead antibiotic moves forward". 31 Oct 2011.
- "Cubist Pharmaceuticals to Acquire Trius Therapeutics". July 2013.
- "FDA approves Sivextro to treat skin infections". June 2014.
- "Sivextro Prescribing info". Lexington, MA: Cubist.Updated March 2015.
- "Tedizolid (TR-701): a new oxazolidinone with enhanced potency". Accessed 2015-03-16.
- Schaadt, R; Sweeney, D; Shinabarger, D; Zurenko, G (August 2009). "In vitro activity of TR-700, the active ingredient of the antibacterial prodrug TR-701, a novel oxazolidinone antibacterial agent". Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 53: 3236–9. doi:10.1128/AAC.00228-09. PMC 2715649. PMID 19528279.
- "Analysis of the Phase 3 ESTABLISH Trials of Tedizolid versus Linezolid in Acute Bacterial Skin and Skin Structure Infections". Accessed March 16, 2015
- "New FDA task force will support innovation in antibacterial drug development". September 2012.
- "Three encouraging steps towards new antibiotics". September 2014.