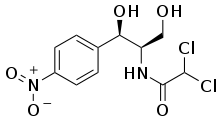
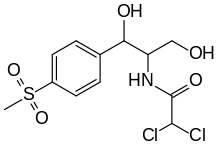
Amphenicol
Amphenicols are a class of antibiotics with a phenylpropanoid structure. They function by blocking the enzyme peptidyl transferase on the 50S ribosome subunit of bacteria.[1]
Examples of amphenicols include chloramphenicol, thiamphenicol, azidamfenicol and florfenicol. The first-in-class compound was chloramphenicol, introduced in 1949. Chloramphenicol was initially discovered as a natural product, but all amphenicols are now made by chemical synthesis.
References
- "APVMA: Florfenicol". Archived from the original on 2007-09-07. Retrieved 2007-07-22.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative
Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.