Posterior ethmoidal artery
The posterior ethmoidal artery is an artery of the head which supplies the nasal septum. It is smaller than the anterior ethmoidal artery.
| Posterior ethmoidal artery | |
|---|---|
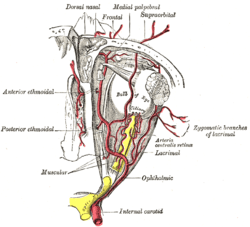 The ophthalmic artery and its branches. (Anterior and posterior ethmoid labeled at left.) | |
| Details | |
| Source | Ophthalmic artery |
| Branches | Meningeal branch Nasal branches |
| Vein | Ethmoidal veins |
| Supplies | Posterior ethmoidal cells Posterior ethmoidal air sinuses Dura mater of the anterior cranial fossa Upper part of the nasal mucosa |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | Arteria ethmoidalis posterior |
| TA | A12.2.06.043 |
| FMA | 49989 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
Course
Once branching from the ophthalmic artery, it passes between the upper border of the medial rectus muscle and superior oblique muscle to enter the posterior ethmoidal canal. It exits into the nasal cavity to supply posterior ethmoidal cells and nasal septum; here it anastomoses with the sphenopalatine artery.
There is often a meningeal branch to the dura mater, while it is still contained within the cranium.
Supplies
This artery supplies the posterior ethmoidal air sinuses, the dura mater of the anterior cranial fossa, and the upper part of the nasal mucosa of the nasal septum.
References
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 570 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
External links
- lesson9 at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University) (nasalseptumart)
- http://www.dartmouth.edu/~humananatomy/figures/chapter_45/45-6.HTM