Olfactory tract
The olfactory tract is a bilateral bundle of afferent nerve fibers from the mitral and tufted cells of the olfactory bulb that connects to several target regions in the brain, including the piriform cortex, amygdala, and entorhinal cortex. It is a narrow white band, triangular on coronal section, the apex being directed upward.
| Olfactory tract | |
|---|---|
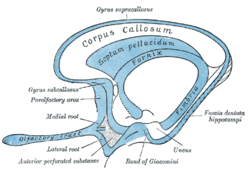 Scheme of rhinencephalon. (Olfactory tract visible at left.) | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | tractus olfactorius |
| NeuroNames | 283 |
| NeuroLex ID | birnlex_1663 |
| TA | A14.1.09.431 |
| FMA | 77626 |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy | |
It lies in the olfactory sulcus on the inferior surface of the frontal lobe, and divides posteriorly into two striae, a medial olfactory stria and a lateral olfactory stria. Fibers of the olfactory tract appear to end in the antero-lateral part of the olfactory tubercle, the dorsal and external parts of the anterior olfactory nucleus, the frontal and temporal parts of the prepyriform area, the cortico-medial group of amygdaloid nuclei and the nucleus of the stria terminalis.[1]
Destruction to the olfactory tract results in ipsilateral anosmia.
Additional images
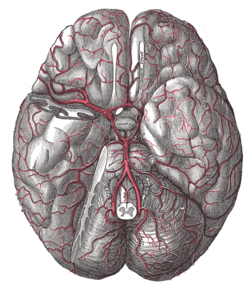 The arteries of the base of the brain.
The arteries of the base of the brain.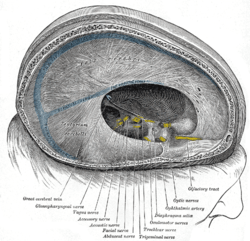 Dura mater and its processes exposed by removing part of the right half of the skull, and the brain.
Dura mater and its processes exposed by removing part of the right half of the skull, and the brain.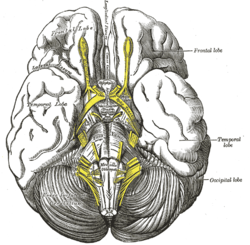 Base of brain.
Base of brain.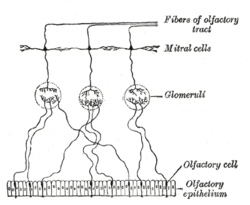 Plan of olfactory neurons.
Plan of olfactory neurons.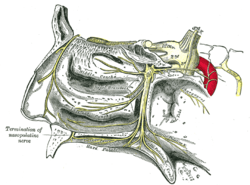 The pterygopalatine ganglion and its branches.
The pterygopalatine ganglion and its branches.- Human brainstem anterior view
 Olfactory nerve
Olfactory nerve- Cerebrum.Inferior view.Deep dissection
- Spinal cord. Brachial plexus. Cerebrum.Inferior view.Deep dissection.
- Spinal cord. Brachial plexus. Cerebrum.Inferior view.Deep dissection.
- Cerebrum. Optic and olfactory nerves.Inferior view. Deep dissection.
- Cerebrum.Inferior view. Deep dissection.
- Cerebrum. Inferior view.Deep dissection
References
- Allison, A. C. (1954). "The secondary olfactory areas in the human brain". Journal of Anatomy, 88 (Pt 4), 481–488.2.
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 826 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
External links
- Atlas image: n1a2p13 at the University of Michigan Health System
- "1-4". Cranial Nerves. Yale School of Medicine. Archived from the original on 2016-03-03.
- "Anatomy diagram: 13048.000-1". Roche Lexicon - illustrated navigator. Elsevier. Archived from the original on 2014-01-01.
- Diagram at thebrain.mcgill.ca