External capsule
The external capsule is a series of white matter fiber tracts in the brain. These fibers run between the most lateral (toward the side of the head) segment of the lentiform nucleus (more specifically the putamen) and the claustrum.
| External capsule | |
|---|---|
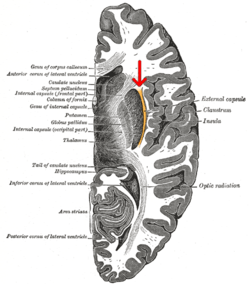 Horizontal section of right cerebral hemisphere. (external capsule shown in orange, indicated by red arrow.) | |
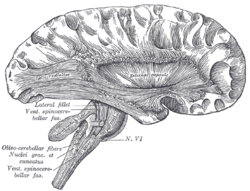 Deep dissection of cortex and brain-stem. (External capsule visible at center.) | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | capsula externa |
| MeSH | D066271 |
| NeuroNames | 253 |
| NeuroLex ID | nlx_16247 |
| TA | A14.1.09.551 |
| FMA | 61959 |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy | |
The white matter of the external capsule contains fibers known as corticocortical association fibers. These fibers are responsible for connecting the cerebral cortex to another cortical area. The capsule itself appears as a thin white sheet of white matter.[1]
The external capsule is a route for cholinergic fibers from the basal forebrain to the cerebral cortex.
The putamen separates the external capsule from the internal capsule medially and the claustrum separates it from the extreme capsule laterally. But the external capsule eventually joins the internal capsule around the lentiform nucleus.
Additional images
 Superficial dissection of brain-stem. Lateral view.
Superficial dissection of brain-stem. Lateral view. Superficial dissection of brain-stem. Ventral view.
Superficial dissection of brain-stem. Ventral view. Dissection of brain-stem. Dorsal view.
Dissection of brain-stem. Dorsal view.- External capsule
- External capsule
- Ventricles of brain and basal ganglia. Superior view. Horizontal section. Deep dissection.
- Ventricles of brain and basal ganglia.Superior view. Horizontal section. Deep dissection.
References
- Powell, Meshell (13 January 2014). "What Is the External Capsule?". wiseGEEK. Conjecture Corporation. Retrieved 22 Jan 2014.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to External capsule. |
- "Anatomy diagram: 13048.000-2". Roche Lexicon - illustrated navigator. Elsevier. Archived from the original on 2014-01-01.
- Image at Univ. of South Carolina