Angular vein
The angular vein is the upper most segment of the facial vein, above its junction with the superior labial vein. It is formed by the junction of the supratrochlear vein and supraorbital vein, runs obliquely downward by the side of the nose, passes under zygomaticus major and joins with the superior labial vein.
| Angular vein | |
|---|---|
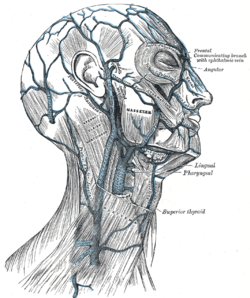 Veins of the head and neck (angular visible at center right.) | |
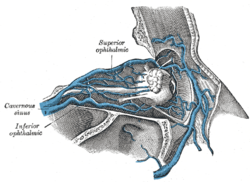 Veins of orbit. | |
| Details | |
| Source | Supraorbital vein |
| Drains to | Facial vein |
| Artery | Angular artery |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | Vena angularis |
| TA | A12.3.05.019 |
| FMA | 50893 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
The angular vein is linked with the cavernous sinus by the superior and inferior ophthalmic veins which are devoid of valves. It receives the lateral nasal veins from the ala of the nose, and the inferior palpebral vein.
Clinical significance
Any infection of the mouth or face can spread via the angular veins to the cavernous sinuses resulting in thrombosis. Since the veins draining this area are valveless and directly join the cavernous sinus, there is a potential risk of spreading infection to the cavernous sinus via these facial veins. This area of the nose is termed the danger triangle. Squeezing the pus from this area should be avoided[1]
Additional images
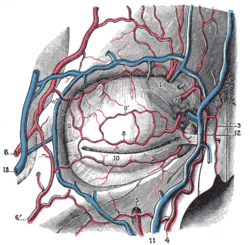 Bloodvessels of the eyelids, front view.
Bloodvessels of the eyelids, front view.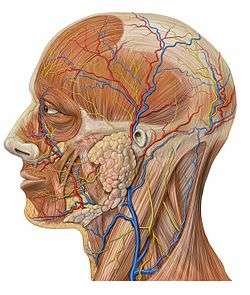 Lateral head anatomy detail
Lateral head anatomy detail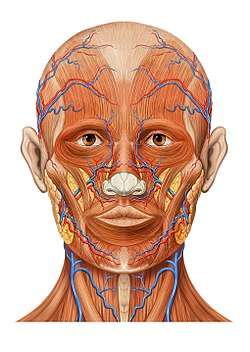 Head anatomy anterior view
Head anatomy anterior view
References
- Önerci, T. Metin (2009). Diagnosis in Otorhinolaryngology. Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg. p. 70. ISBN 978-3-642-00498-8.
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 645 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)